This article deep dive into how conjoint analysis is used understanding the important and most fundamental aspect of marketing which is consumer preferences.
It is based on the simple premise that consumers evaluate the value of an object (real or hypothetical) by combining the separate amounts of value provided by each attribute.
Utility, a subjective judgment of preference unique to each individual, is the most fundamental
concept in conjoint analysis and the conceptual basis for measuring value.
-
encompasses all features of the object, both tangible and intangible.
-
the value placed on each of the levels of the attributes. In do- ing so, respondents react to varying combinations of attribute levels
$Utility = Beta1 * attribute1 + Beta2 * attribute2+ Beta3 * attribute3+ …$
Utility basically tells us whether a customer gonna buy a product or not.
To understand how part worth utility is calculated
How to decide what attributes are needed to design
-
What are the important attributes that could affect preference? (Brand , Price)
-
How will respondents know the meaning of each factor? — (Level :Brand X or Brand Y, 30 cents, 40 cents, 50 cents)
-
What do the respondents actually evaluate? (Profile: Brand X at 40 cents)
-
How many profiles are evaluated? (Design: The selection of number of profiles)
HYPOTHETICAL EXAMPLE OF CONJOINT ANALYSIS
We will perform conjoint analysis on the preference choice of two brands of smart phone Apple and Samsung with 3 attributes and each attributes has only two levels.
Attributes and Levels
-
Brand: Apple, Samsung
-
Camera Quality: High, Medium
-
Price: $1000, $800
-
Charging Speed: Fast, Standard
Possible Product Profiles
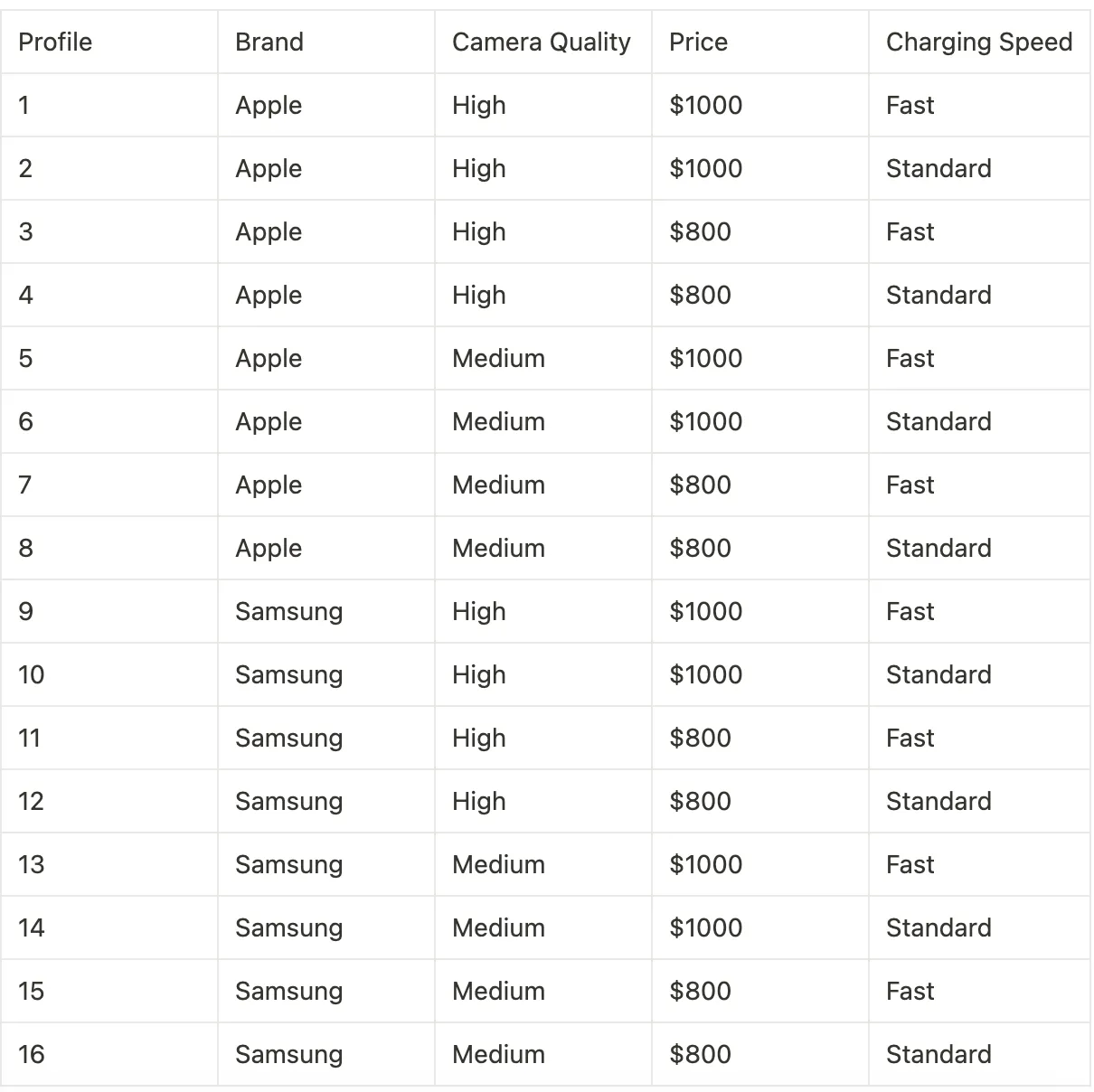
Survey based on customer preference of a smart phone
Hypothetical Survey
Here are the rankings from two respondents for each profile:
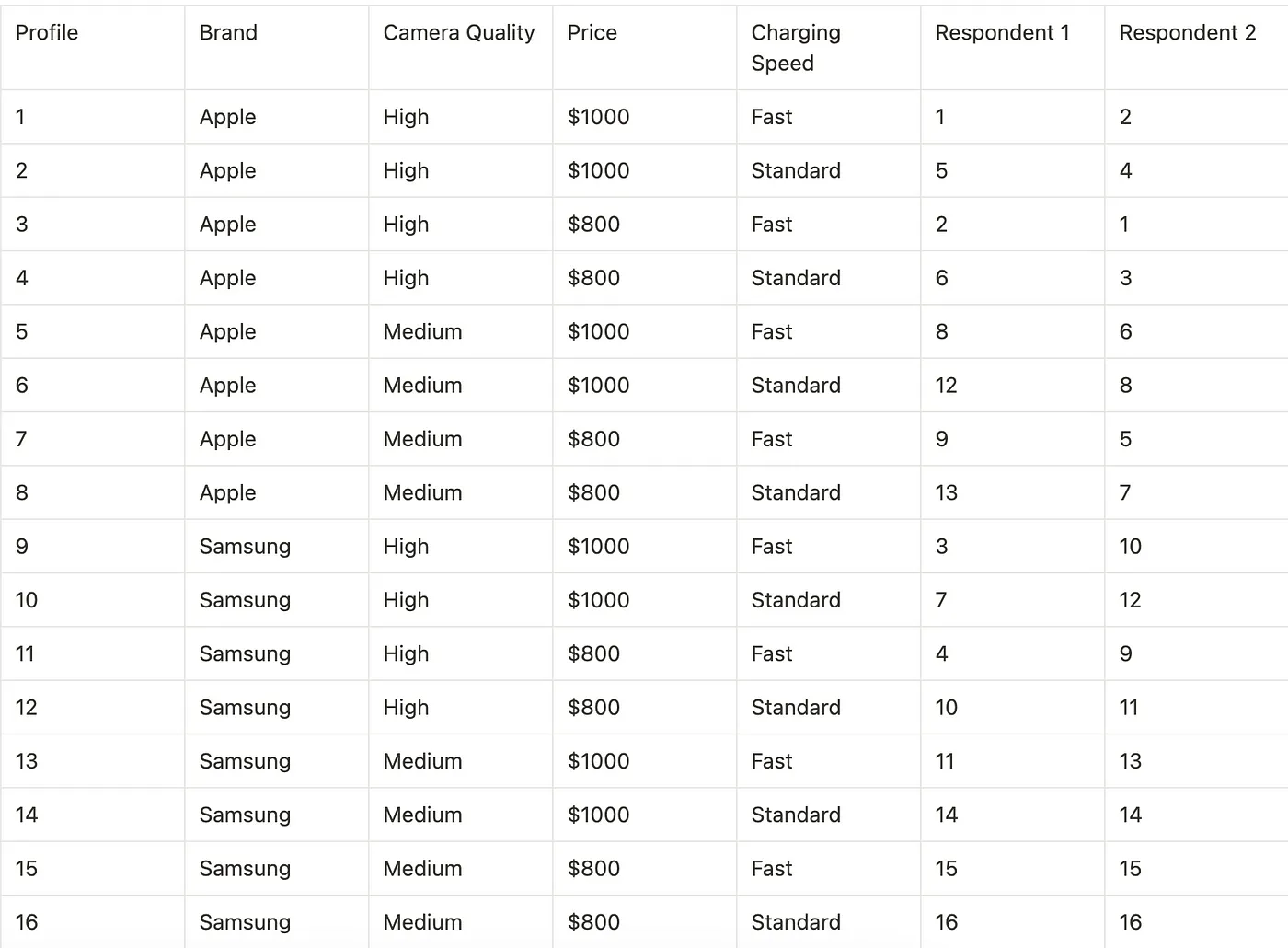
Analysis
Calculating the part worth utility of each attribute
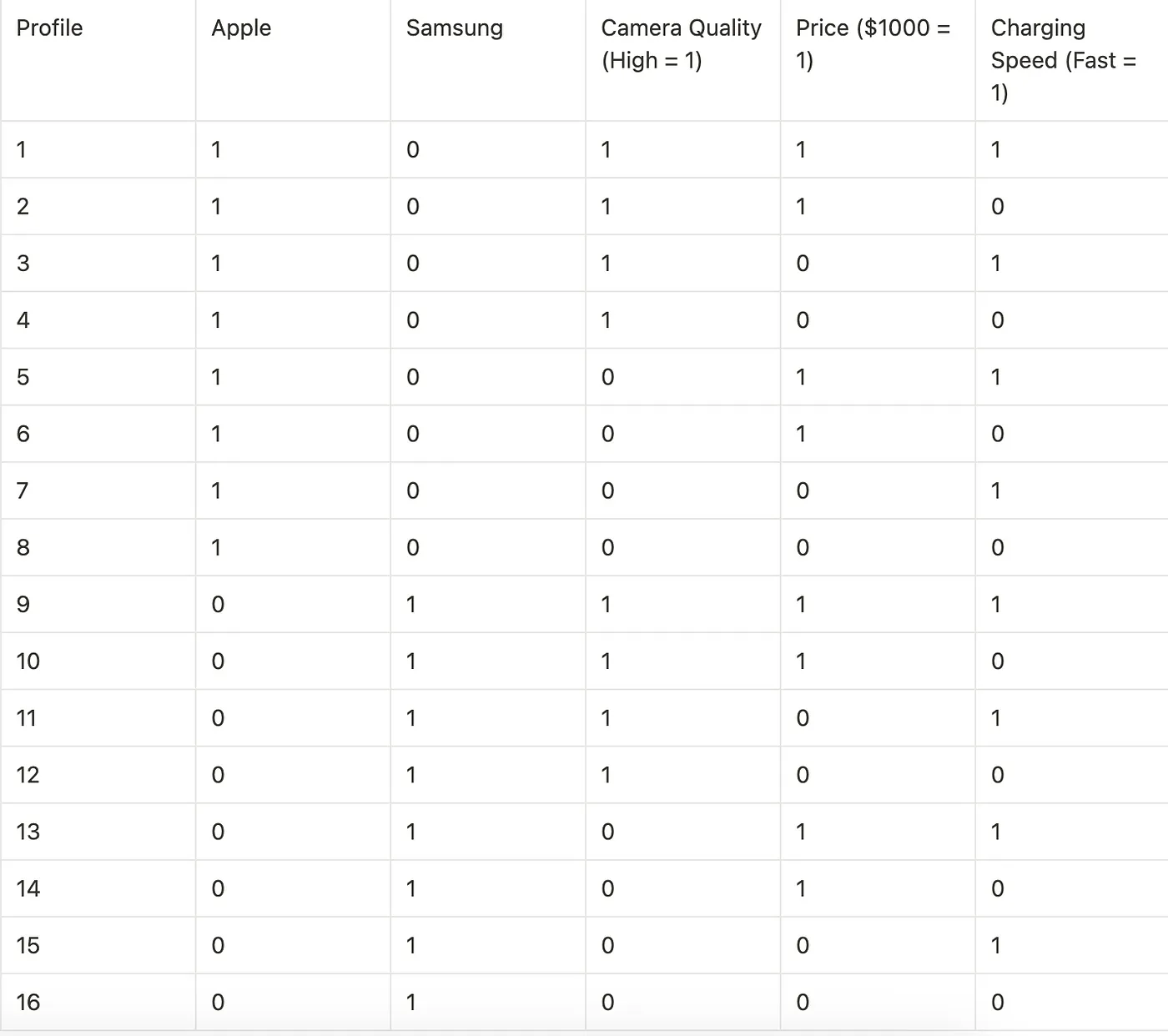
To calculate the part worth utility of the attribute we need to design Design Matrix
Step 1: Design Matrix
Step 2: Collect Preference Data
We already have the preference data from each of the customer.
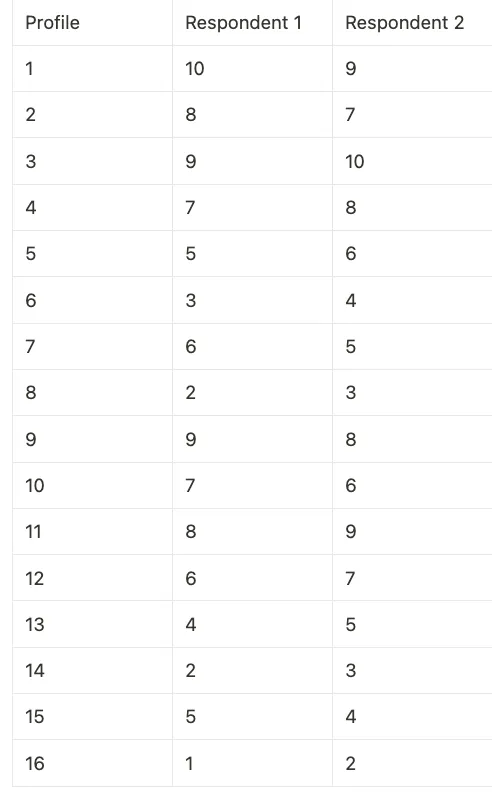
Step 3: Run Regression Analysis
We need to run regression on each of the profile .
The regression equation would look like this:
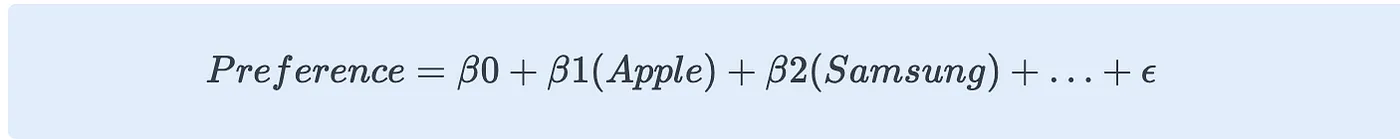
Step 4: Interpret Coefficients
Assume the regression analysis provides the following coefficients for the first respondent
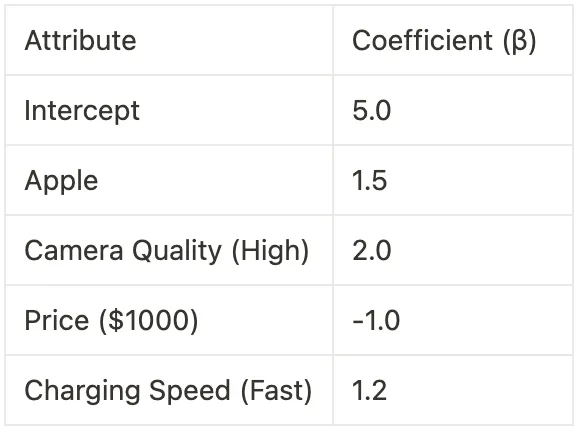
The part-worth utility for the brand attribute (Apple) is 1.5. This means that, all else being equal, respondents prefer Apple over Samsung by a utility value of 1.5.
By following these steps, you can calculate the part-worth utility for the brand attribute in a conjoint analysis.
Step 5: Estimating Part-Worths and Factor Importance for Respondents 1
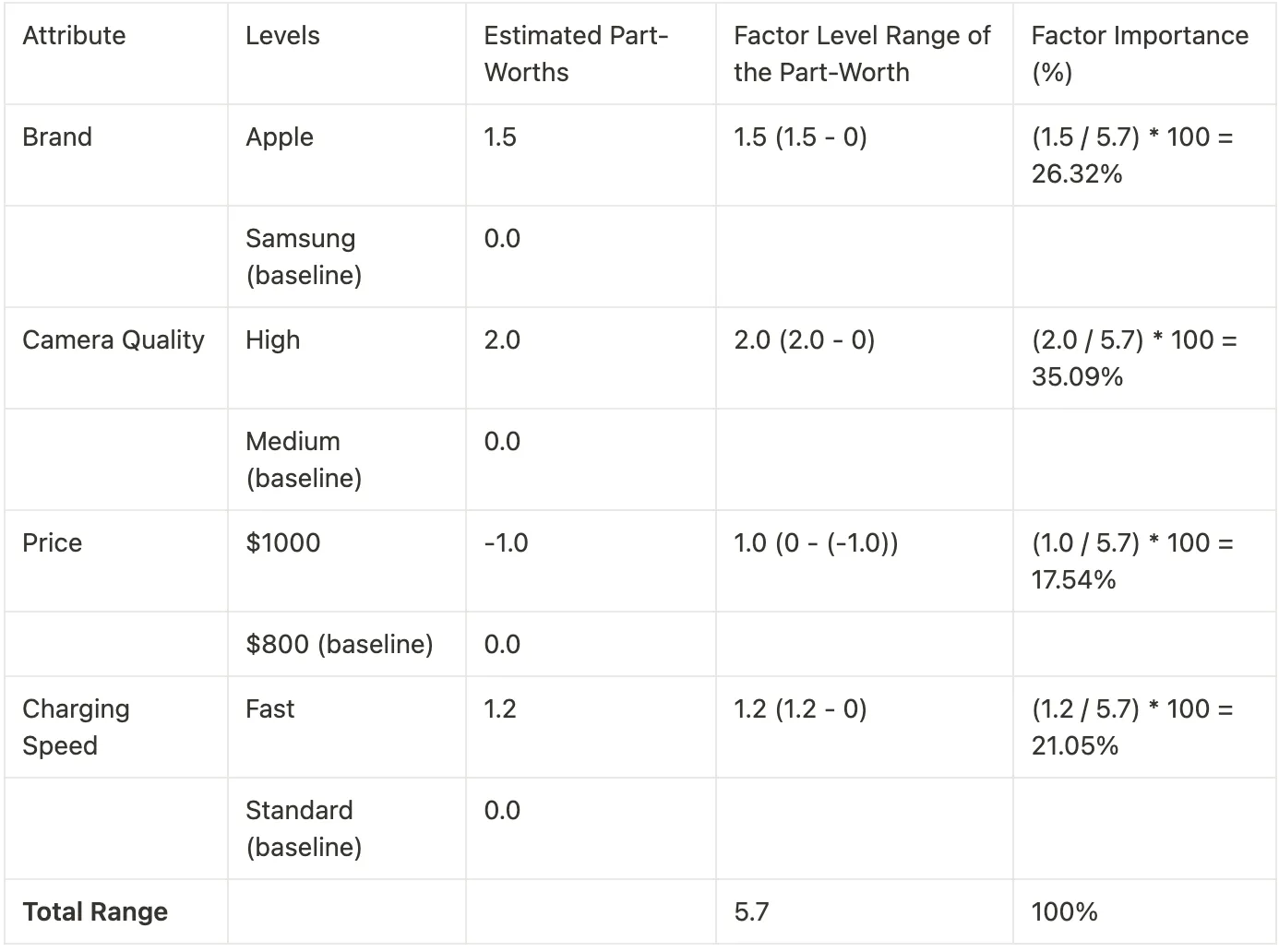
From the above table we can conclude that most important factor for Customer 1 to make a purchase is camera quality with factor importance of 35.1%.
Comparison of Conjoint Analysis with other analysis
Compositional Versus Decompositional Techniques
Conjoint Analysis is decompositional technique. Mostly in compositional technique market researcher collects the data and rating and try to run the regression for the rating and find the relation.
In decompositional all what is needed is the preference toward certain profile and inference toward that customer can be made.
Specifying the Conjoint Variate
conjoint variate is a linear combination of effects of the independent variables (levels of each factor) on a dependent variable. The important difference is that in the conjoint variate the researcher specifies both the independent variables (factors) and their values (levels). The only information provided by the respondent is the dependent measure
Separate Model for each customer
One the main advantage of Conjoint analysis is we can build a specific model for each customer. It will help to understand customise our marketing strategy for them. The other analysis model uses each customer as a single point and build a model for general purpose.
**Disaggregate Model **— When the analysis is done on each customer
**Aggregate Model **— When the analysis is done on a group of customers.
Flexibility in Types of Relationships
In most of the analysis the relationship between dependent and independent variable is linear but in conjoint there is no such assumptions.
How to perform Conjoint Analysis
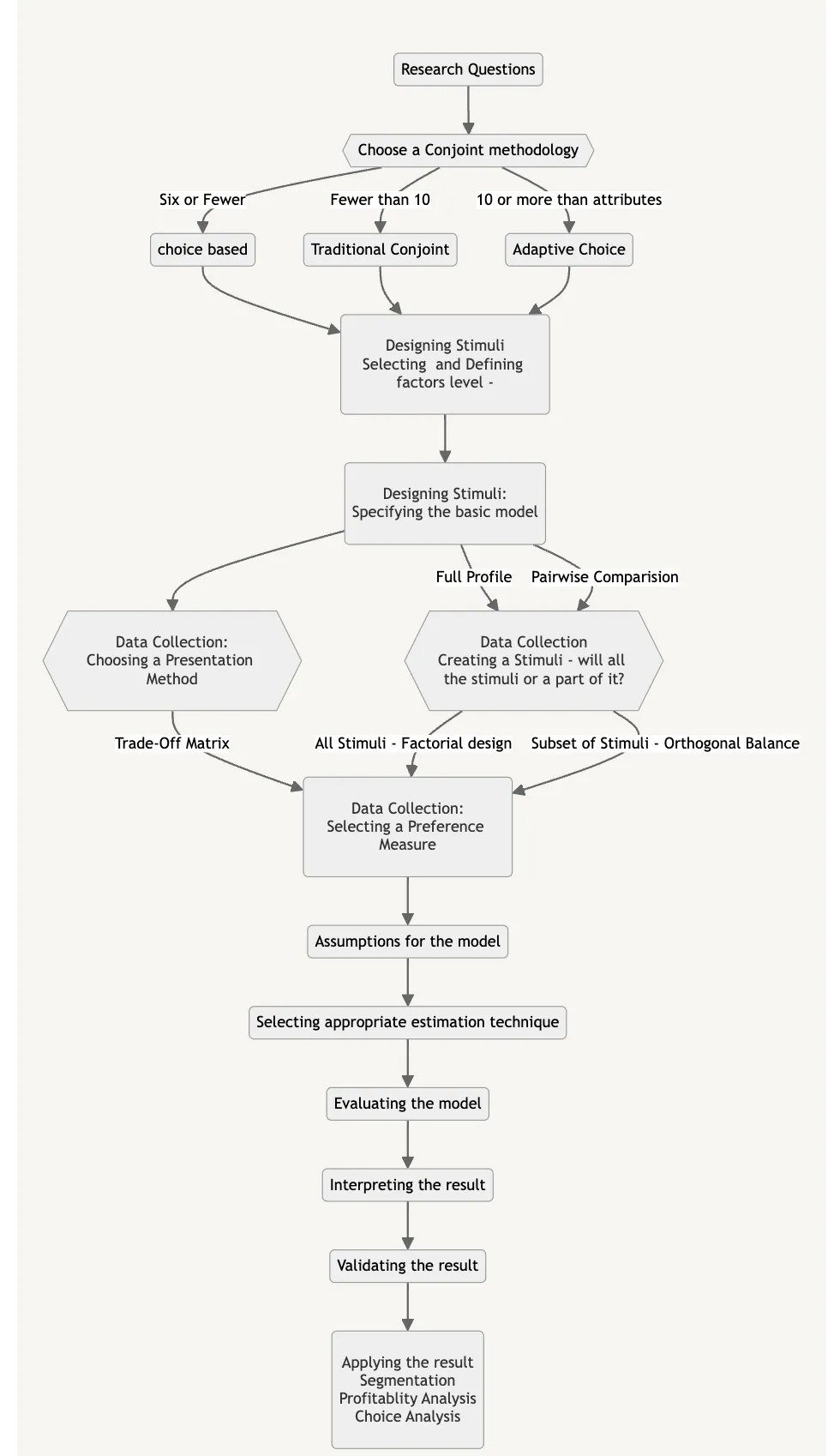
This is the small introduction how conjoint analysis can be useful in creating your marketing strategy for customer.




评论 (0)