
Brief Overview of the Cryptocurrency Market
Cryptocurrency has become a big player in the world of money, changing how we think about finances.
With Bitcoin leading the charge and tons of other altcoins popping up, more and more people are looking for safe and easy places to buy and sell them.
This is where Centralized Exchanges (CEXs) come in.
They're kind of like stock exchanges but for crypto, letting users trade these digital assets smoothly.
Here's a cool fact: As of May 4, 2024, the total market value of all cryptocurrencies is over $2,334,591,090,589 ($2.46 Trillion), showing just how big this market has become!
CEXs play a key role in making this market work.
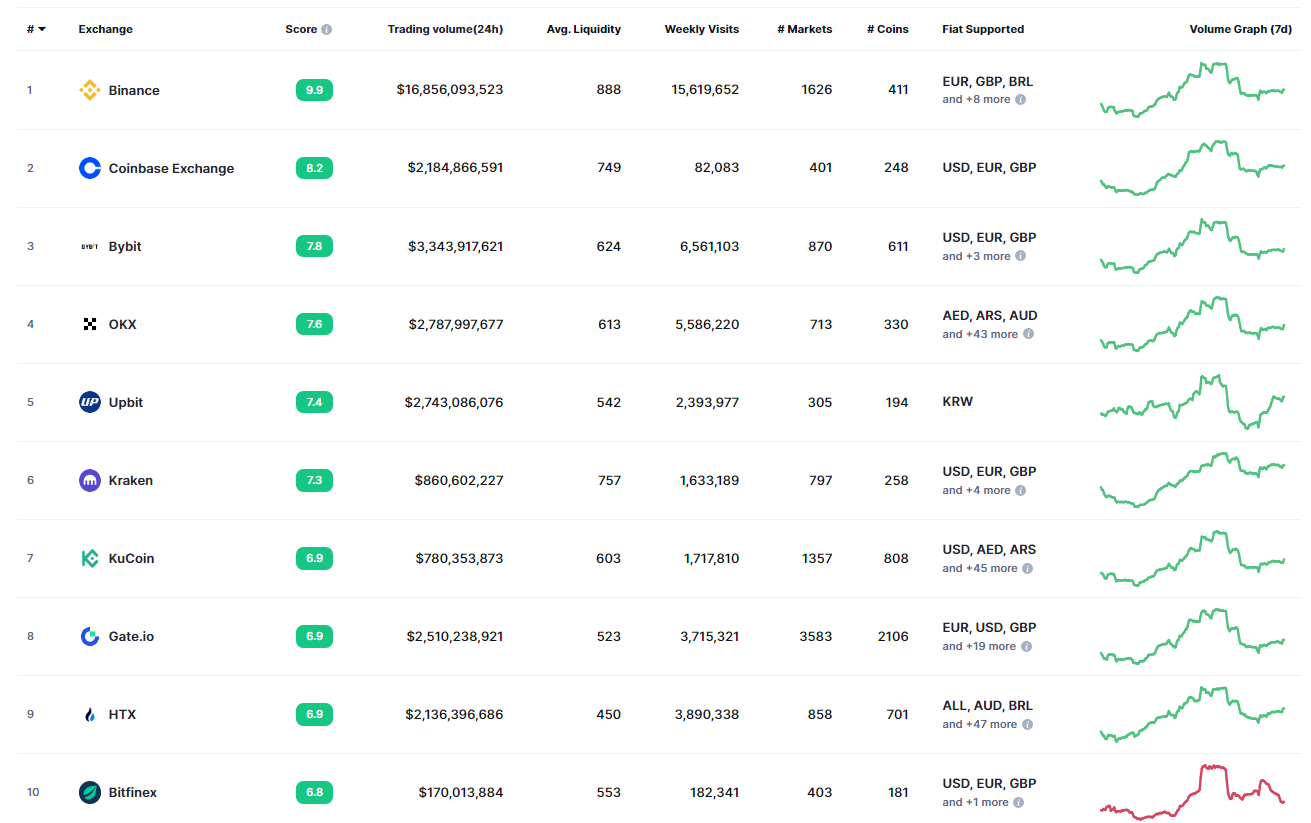
Let's explore what CEXs are all about and why they're important in the world of cryptocurrencies.
Why Centralised Exchanges are better?
Choosing the right platform to buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrency can be tricky.
Here's a breakdown of the three main exchange types:
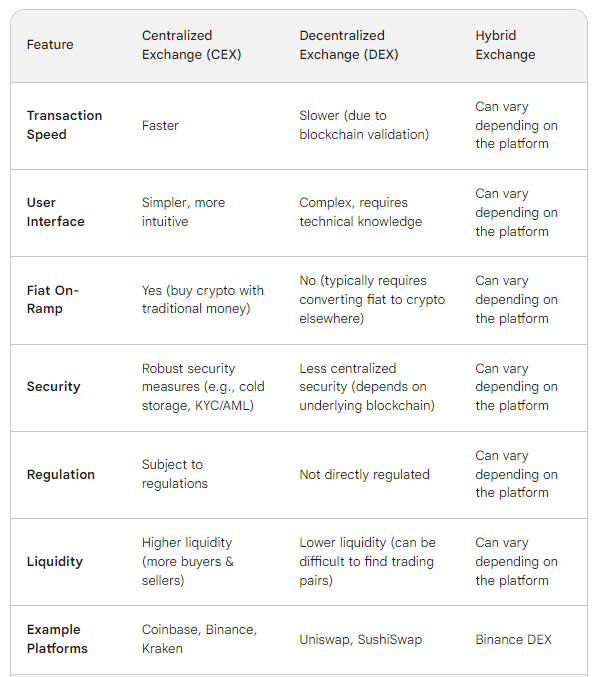
Core Components of a CEX Platform:
Matching Engine
The matching engine is like the brain of a CEX platform. Its main job is to make sure that when someone wants to buy cryptocurrency, they get matched with someone who wants to sell it, so trades can happen smoothly.
How it Works:
The matching engine constantly receives two main types of orders from users:
-
Buy Orders: These specify the maximum price a user is willing to pay for a certain amount of cryptocurrency.
-
Sell Orders: These specify the minimum price a user is willing to accept for selling a certain amount of cryptocurrency.
The matching engine uses clever algorithms to analyze these orders and find the best fit.
Here are two common matching algorithms used in CEX platforms:
Central Limit Order Book (CLOB):
The Central Limit Order Book (CLOB) is essentially a structured list where buy orders and sell orders are organized based on their prices. Sell orders with the lowest prices are placed at the top, while buy orders with the highest prices are also at the top on their side.
The matching engine continuously checks this list, seeking orders where the buy price is equal to or higher than the sell price. Once a match is found, the trade executes at the price of the sell order.
This method ensures that the market price accurately reflects the supply and demand dynamics from all users, akin to an auction where the highest bidder succeeds only if their bid meets the minimum ask.
Benefits:
-
Facilitates fair price discovery
-
Provides transparency for users to observe current buy and sell offers
Drawbacks:
- This can result in slower trades if there aren't perfect matches with existing orders
Market Order Book (MOB):
The MOB method simplifies the trading process by allowing users to specify the amount of cryptocurrency they want to buy or sell. The matching engine then locates the best available price based on the current order book.
When a user submits a market order, the matching engine may fulfill it by combining multiple smaller orders at various prices. This ensures quick execution but may not always result in the optimal price.
Benefits:
-
Fast order execution
-
Simplified process for users who prefer not to set specific order prices
Drawbacks:
-
Users may not obtain the best price available
-
Limited visibility into order book details
Real-World Example:
Imagine you're on a CEX platform, wanting to buy 1 Ethereum (ETH) for $3,000.
Here's how the matching engine might handle it:
Scenario 1 (CLOB): The engine spots a seller offering 1 ETH at $3,001. You get your ETH, but you pay a bit more than your target price. This trade helps figure out the current value of ETH in the market.
Scenario 2 (MOB): Another buyer already placed an order to buy 1 ETH, even if they wanted it for less than $3,000. The engine completes its order first, so you might need to adjust your price or wait for another seller.
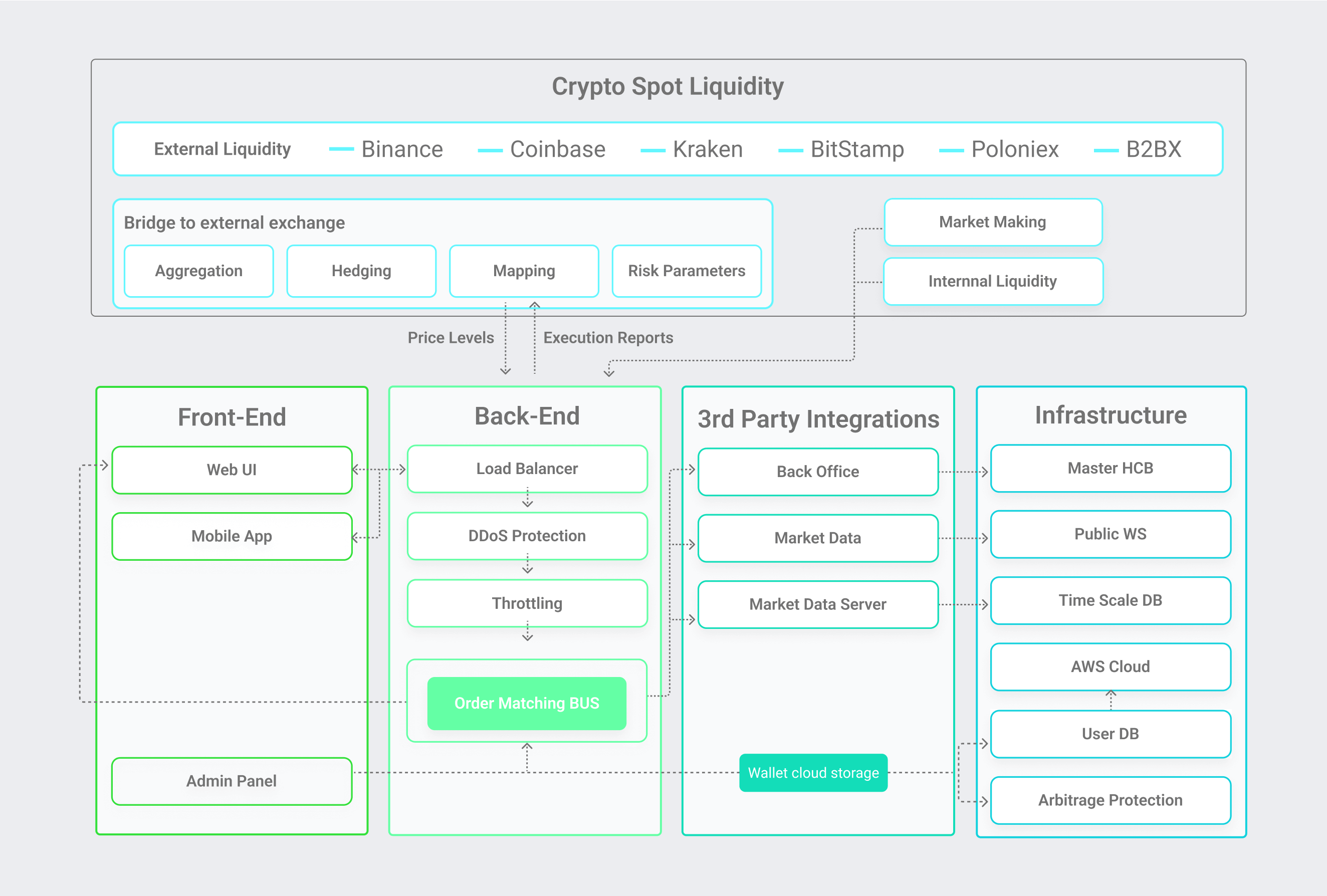
Trading Engine
A trading engine manages all the actions involved in buying or selling cryptocurrencies, functioning much like a highly efficient and secure matchmaker, such as:
Order Management:
This includes handling buy and sell orders from users. Users can place orders to buy or sell a specific amount of cryptocurrency at a certain price.
-
Order Placement: Users can submit their orders, saying how much cryptocurrency they want to buy or sell and at what price.
-
Order Modification: Users can change their orders if they want to buy or sell at a different price or amount.
-
Order Cancellation: If users change their minds or if market conditions change, they can cancel their orders before they are executed.
Trade Execution:
Once the trading engine finds matching buy and sell orders, it completes the trade by transferring the cryptocurrency between user accounts.
-
Matching Orders: The engine looks for buy orders that match sell orders (or vice versa) based on price.
-
Trade Completion: It then carries out the trade, transferring the cryptocurrency between users.
Trade Settlement Mechanisms:
To make sure trades between users are safe and reliable, CEX platforms use different methods to settle trades securely.
Atomic Swaps: These are trades between users that happen without needing to trust a central authority.
How it works:
-
Users lock their assets (cryptocurrency and fiat money) in smart contracts.
-
The smart contracts only release the assets if both sides of the trade happen at the same time.
-
This stops one person from cheating the other.
Payment Channels:
These let users send lots of transactions to each other without needing to use the main blockchain every time.
How it works:
-
Users put money into the channel at the start.
-
Then, they can send lots of transactions to each other without needing to wait for each one to be confirmed on the blockchain.
-
This saves time and money.
Wallet System
Cryptocurrency wallets are like digital safes for your digital money. Instead of holding physical cash, they keep your cryptographic keys safe.
Tiered Wallet Structure:
CEXs leverage a tiered wallet system, utilizing a combination of:
-
Hot Wallets: These online wallets facilitate quick deposits, withdrawals, and trading activity. However, their internet connectivity increases vulnerability to cyberattacks.
-
Cold Wallets: These offline, air-gapped wallets provide superior security for storing the majority of user funds. Their offline nature significantly reduces hacking risks.
Advanced Security Measures:
CEXs go beyond basic security practices to safeguard user assets. Here are some prominent methods:
Encryption:
-
Standard Encryption: CEXs use AES-256 and similar encryption algorithms to protect private keys and account info. These algorithms make data unreadable without the decryption key.
-
Data Security: Encryption is applied to stored data and during transmission, ensuring continuous protection of user information.
Benefits:
-
Enhanced Security: Encrypted data remains unreadable, even in a breach, safeguarding user funds.
-
User Confidence: Strong encryption builds trust, allowing users to securely store their assets.
Multi-Signature Technology:
Shared Responsibility: Critical transactions require approval from multiple authorized parties, reducing the risk of fraud or unauthorized access.
- Enhanced Security: Requiring multiple approvals adds layers of security, making it harder for malicious actors to access funds.
Benefits:
-
Reduced Fraud Risk: Multiple approvals deter unauthorized transactions.
-
Improved Accountability: Multi-signature tech ensures clear transaction trails, fostering transparency.
Regular Security Audits:
-
Independent Testing: CEXs regularly engage security firms to conduct penetration testing, identifying and addressing vulnerabilities.
-
Vulnerability Assessment: Early detection of weaknesses allows prompt patching and system updates, strengthening overall security.
Benefits:
-
Early Detection: Regular audits catch vulnerabilities before they're exploited.
-
Continuous Improvement: Proactive measures enhance the platform's security over time.
Fund Management:
-
Deposits and Withdrawals: The wallet system facilitates smooth deposits of various supported assets into user accounts. Likewise, it enables secure withdrawals through a defined process.
-
Transaction Tracking: Users have access to a detailed transaction history within their wallet. This provides complete transparency and allows for easy monitoring of account activity.
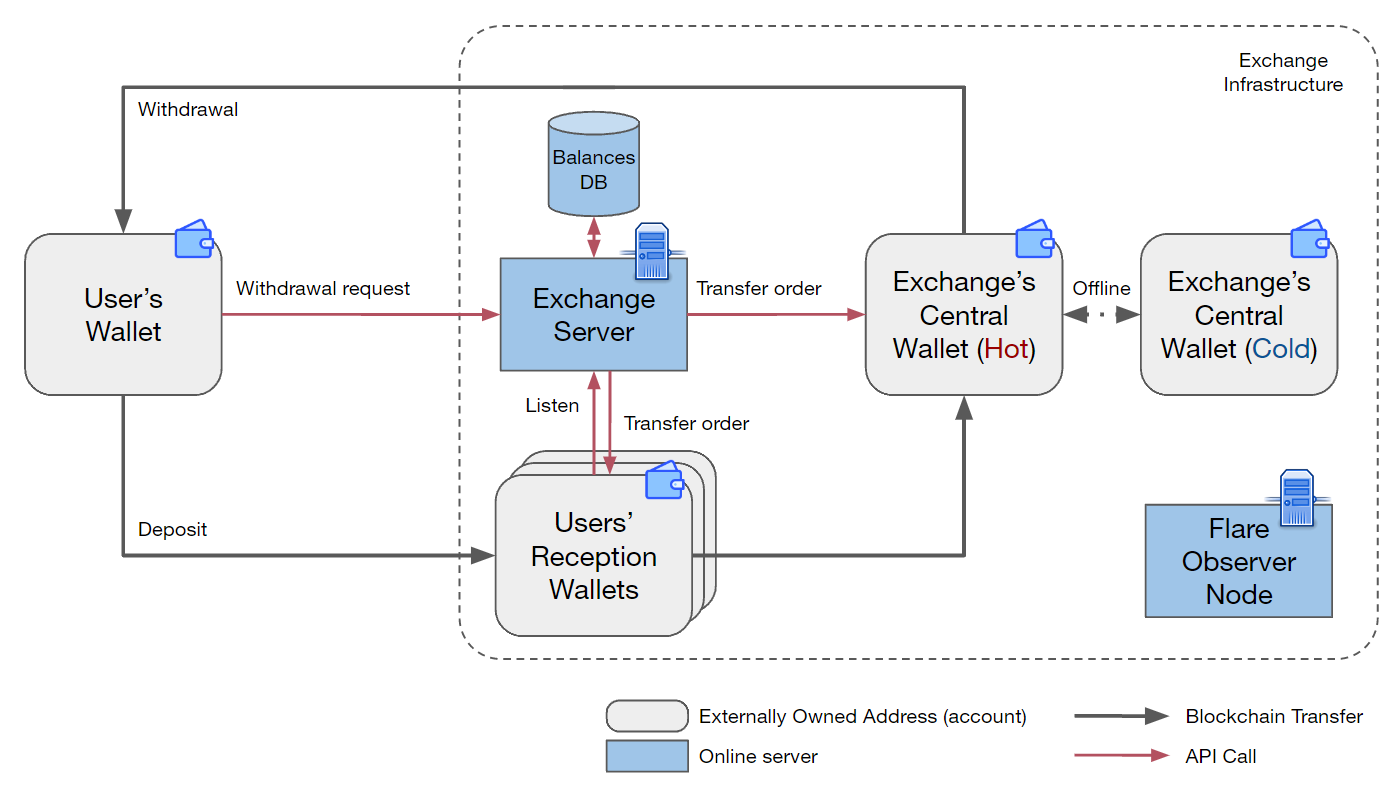
User Management System
User Management System (UMS) acts as the central hub for all user interactions, from the initial signup process to managing trading activities.
Account Creation
The first step for users on a centralized exchange (CEX) is registering for an account. This involves providing important details:
-
Email Address: Used for account verification, password resets, and important updates.
-
Username: A unique name for logging in and using the exchange.
-
Password: The first line of defense for account security. Strong passwords with a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols are recommended.
The User Management System (UMS) securely collects and stores user information. It uses encryption to keep sensitive data safe.
KYC/AML Compliance
To prevent financial crimes like fraud and money laundering, CEXs must follow KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) regulations. The UMS helps with this by:
-
Identity Verification: Users provide documents like passports or IDs to prove who they are.
-
Transaction Monitoring: The system watches for suspicious activity, like large deposits or unusual trades.
-
Risk Assessment: Based on user data, accounts may be flagged for further checks to reduce risks.
User Access Control
Once registered and verified, users need permission to do things on the exchange. The UMS controls this by assigning roles:
-
Basic User: Can view market data and account balances.
-
Trading User: Can buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies.
-
Advanced User: May access features like margin trading or staking, depending on the CEX.
Advanced Features
Margin Trading
It allows you to Borrow funds from the exchange to increase your buying power. Magnify potential profits (and losses).
Architecture:
-
Risk Management Engine: This system assesses your eligibility for margin based on factors like account balance, collateral requirements (crypto you hold as security for the loan), and risk tolerance.
-
Loan Origination System: Manages borrowing and lending. It allocates borrowed funds to your account and tracks loan repayments with interest.
-
Liquidation Engine: Monitors your positions in volatile markets. If the value of your holdings falls below a certain threshold (maintenance margin), the system automatically sells assets to cover the loan and prevent further losses.
Margin trading is a high-risk strategy. Only use it if you fully understand the risks involved and have a well-defined risk management plan.
Staking & Lending
It allows you to generate passive income on your crypto holdings through staking and lending.
Staking:
Lock up your holdings of Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains to support the network and earn rewards.
Architecture:
- Staking Module: This component interacts with supported PoS blockchains to validate your holdings and distribute staking rewards directly to your account.
Lending:
Lend your crypto to other users or to the exchange itself, earning interest on your holdings.
Architecture:
-
Lending Pool: A secure pool holds deposited crypto assets. The platform matches lenders with borrowers based on pre-defined parameters like interest rates and loan terms.
-
Interest Rate Engine: Calculates and distributes interest earned on lent assets based on market conditions and lending agreements.
Advanced Order Types
It offers advanced order types to provide you with greater control and flexibility over your trades:
-
Trailing Stop-Loss: Automatically adjusts the stop-loss price to trail behind a rising asset price, protecting profits while allowing for some upward movement.
-
Iceberg Orders: Only reveal a portion of the total order size initially, helping to mask trading intentions and potentially achieve better order execution.
Architecture:
-
Order Management System (OMS): The core component responsible for receiving, validating, and processing all order types, including advanced orders. The OMS interacts with the matching engine to find counterparties for your trades.
-
Order Routing Engine: Efficiently routes orders to the appropriate venue (internal order book or external liquidity sources) based on the order type and your chosen execution strategy.
Third-Party Integrations
integrate with various third-party tools to cater to diverse trading styles and broaden user functionality.
Examples:
-
Trading Bots: Automate trading strategies based on pre-defined rules and technical indicators.
-
Charting Tools: Offer advanced charting functionalities for technical analysis and market visualization.
-
Market Data Providers: Integrate real-time and historical market data feeds for comprehensive market insights.
Architecture:
-
API Gateway: Provides a secure and standardized interface for third-party applications to interact with the exchange's data and functionalities.
-
Authentication Service: Manages API keys and access permissions for third-party tools, ensuring secure data access.
Technical Considerations
Choosing the right programming languages and frameworks is crucial for building a robust and scalable CEX platform. Popular choices include:
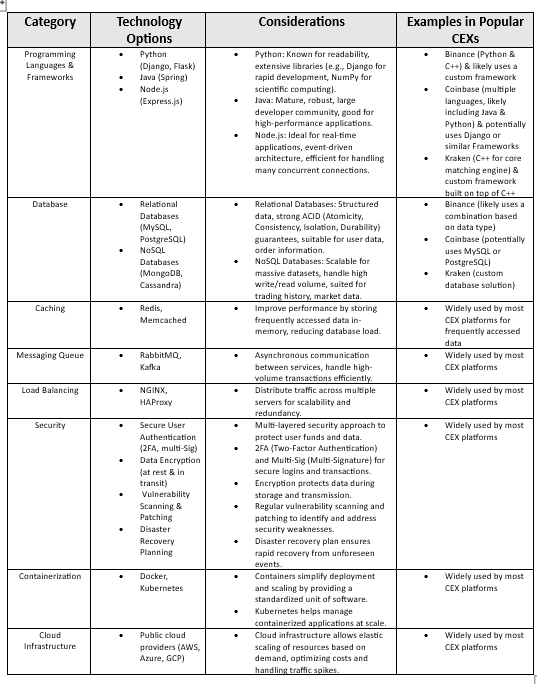
Scalability Considerations:
-
Horizontal Scaling: Ability to add more servers to handle increased load. Technologies like NoSQL databases, messaging queues, and load balancing facilitate this.
-
Microservices Architecture: Breaking down the platform into smaller, independent services improves maintainability and individual service scalability.
-
Cloud Infrastructure: Cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or GCP offer on-demand resources and elastic scaling capabilities.
Choosing the right tech stack depends on specific CEX platform needs. Consider factors like:
-
Transaction Volume: Expected number of trades per second.
-
Data Storage Requirements: Amount and type of data to be stored (user data, order history, market data).
-
Security Priorities: Level of security required to protect user funds and sensitive data.
Want to Build Binance Clone?
Considering the potential of Centralized Exchange, you might be interested in creating a similar platform. We can help you get started quickly!
Our Advantages:
-
Pre-Built Solution: We’ve already developed and tested a robust Centralized Exchange platform, saving you significant time and resources.
-
Faster Deployment: Leverage our existing solution for a faster launch compared to building from scratch.
-
Customization Options: We can tailor the platform to your specific needs and preferences.
Centralized Exchange User Panel DEMO: https://ordersbook.demo-crypto.com/
(Go to - Sign In and Login to Experience)
Centralized Exchange Admin Panel DEMO: https://adminordersbook.demo-crypto.com/
If you’re interested in learning more about our pre-built Centralized Exchange solution, feel free to contact us.
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/akashkumar107/
Telegram: Akash_kumar107
We’d be happy to discuss your requirements and provide further details.
Conclusion
Building a secure and scalable CEX platform is a complex undertaking. By prioritizing market research, leveraging cutting-edge technology, implementing robust security measures, and offering a user-friendly experience, your CEX can become a trusted gateway for users to navigate the exciting world of digital assets.




评论 (0)