The collapse of FTX in November 2022 underscored the critical vulnerabilities plaguing centralized exchanges (CEXs), including the safety of customer deposits, susceptibility to hacks, privacy concerns, restrictive withdrawals, and high fees. This event catalyzed a significant shift towards self-custody and decentralized trading solutions. As traders increasingly prioritize security and self-custody of their assets, decentralized exchanges (DEXs) have gained prominence, offering a robust alternative that eliminates intermediaries and allows direct peer-to-peer trading in a non-custodial manner.
This shift to DEXs not only enhances user autonomy but also drives innovation in trading models, with the central limit orderbook (CLOB) and the automated market maker (AMM) emerging as the two predominant frameworks in the DeFi landscape. This article will explore these frameworks, providing a detailed comparison and discussing how they redefine the trading experience.
What is a Central Limit Orderbook (CLOB)?
A central limit orderbook (CLOB) DEX borrows a trading structure familiar in TradFi and CeFi markets. In this structure, a CLOB collects and matches buy and sells orders in a single ledger. Thus, a CLOB is made of layers of buy and sell orders submitted by traders. These orders represent the prices at which traders are ready to buy or sell assets, creating a detailed map of market demand and supply at different price points.
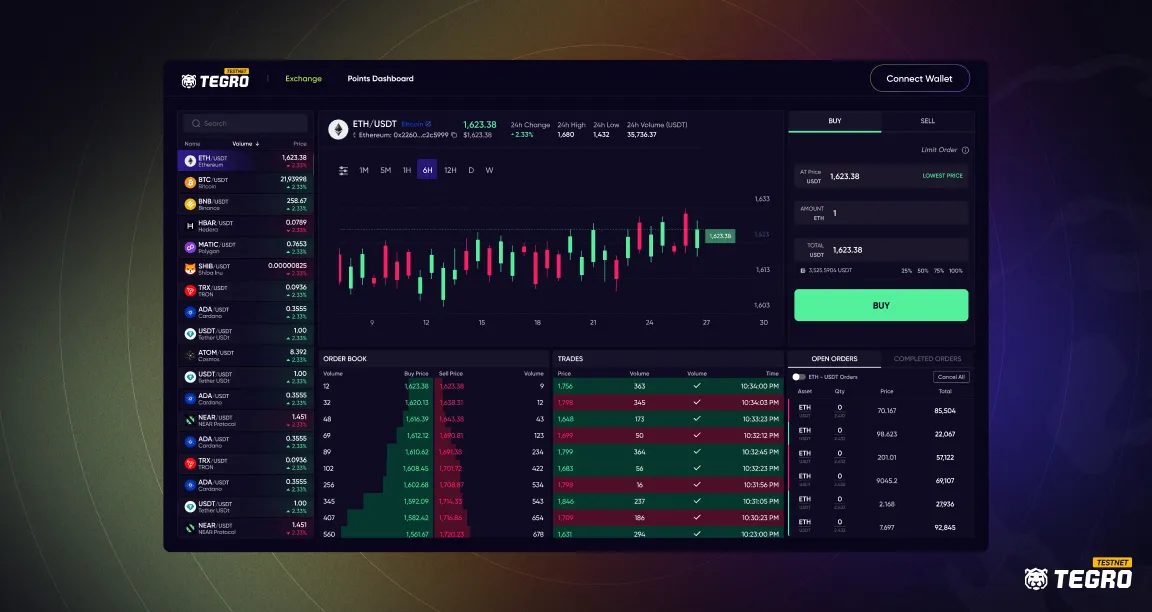
Advantages of Central Limit Orderbooks
-
Transparency: The CLOB provides complete visibility of all order depths, which includes buy and sell orders at various prices. This transparency helps traders make informed decisions based on market demand and supply.
-
Price discovery: The market price in a CLOB is determined by the lowest available sell order (ask) and the highest buy order (bid). This mechanism ensures efficient price discovery as it reflects the most immediate willingness of the market participants to trade.
-
Capital efficiency: CLOBs facilitate single-sided liquidity, which reduces the burden on market makers to deploy extensive asset collaterals.
-
Zero slippage: CLOBs prevent price discrepancies by enabling traders to place limit orders that specify the exact price they wish to buy or sell.
-
No MEV bot interference: Using transaction sequencing, CLOBs ensure that orders are executed in the exact order they are received, preventing bots from manipulating order execution for profit and safeguarding traders from potential front-running, sandwich and other exploitative strategies.
What is an Automated Market Maker?
Automated Market Makers (AMMs) represent an “over-the-counter” approach to asset exchange in DeFi. AMMs do not match buyers and sellers, instead liquidity for both sides of a trading pair are collected into a common pool. The market price is determined by an algorithmic formula that calculates the relative availability of assets within the liquidity pool and adjusts the price accordingly.
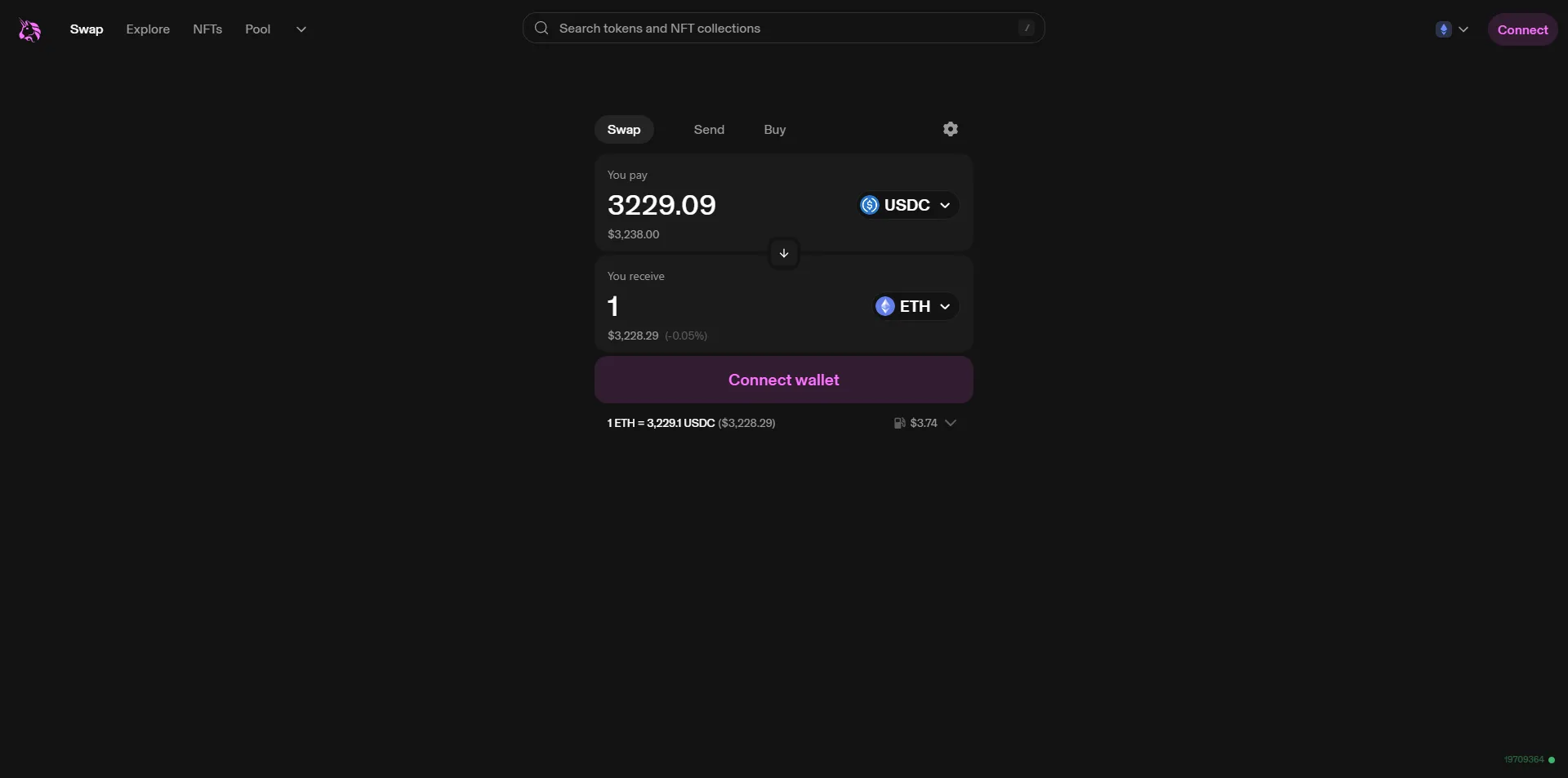
Advantages of Automated Market Makers
-
No counterparty required: By leveraging liquidity pools, AMMs ensure that liquidity is always available without the requirement of a trading counterparty’s presence.
-
Yield opportunities: By depositing assets into liquidity pools, participants can earn fees from the trades that occur within the pool, proportional to their contribution.
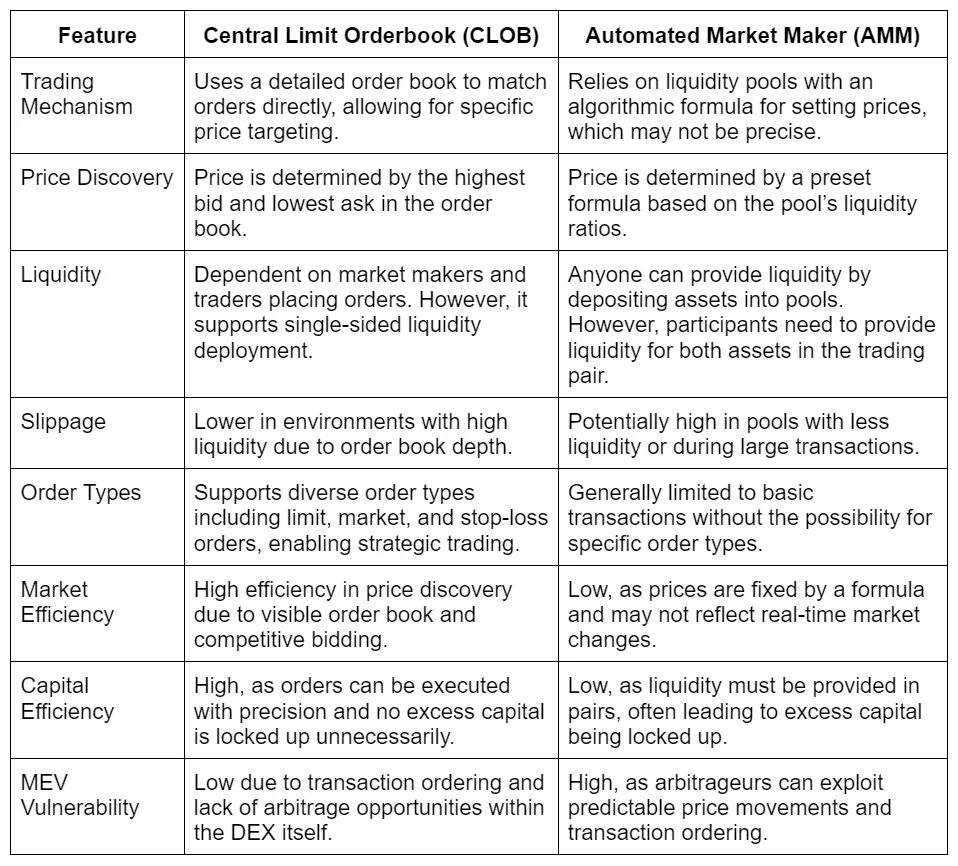
Is a Central Limit Orderbook better than an Automated Market Maker?
As the DeFi landscape is evolving, the choice of trading mechanism can significantly impact both the user experience and the market effectiveness. Right now, Central Limit Order Books (CLOBs) and Automated Market Makers (AMMs) stand out as prominent frameworks. This section delves into a detailed comparison of these two models, highlighting key features and differences to explore which system might be more advantageous for DeFi participants.
Conclusion
In the DeFi ecosystem, AMMs and CLOBs play distinct yet complementary roles that collectively enhance market efficiency and accessibility. AMMs are particularly beneficial for trading pairs with higher spreads and lower frequency, offering essential liquidity that ensures traders can always find a counterparty — a feature that is invaluable for those dealing in less popular tokens. As depicted in the accompanying infographic, AMMs cater to retail traders with wider spreads, accommodating large size orders that may not be as frequent but are crucial for market access. However, these wider spreads indicate poorer price discovery and less efficient market making, which can limit the use of complex trading strategies.
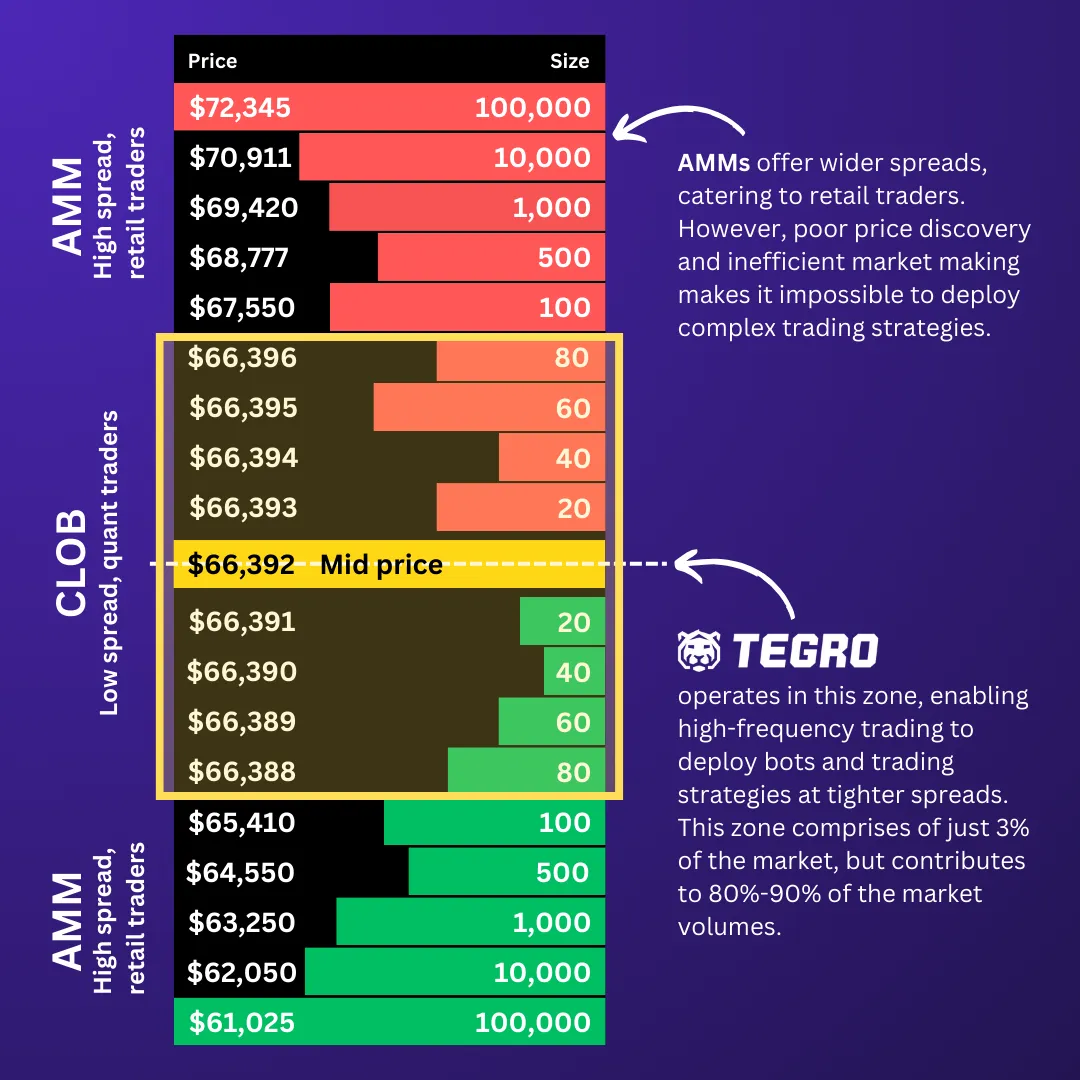
On the other hand, CLOBs cater to a different segment of the market — primarily, the high-frequency traders who seek competitive platforms for executing orders. Operating close to the mid-price, CLOBs offer tighter spreads and lower costs, which are key for strategies that require high speed and precision. This environment is conducive to deploying bots and trading strategies that operate within these thin margins. Although this space constitutes just a fraction of the market, it contributes to a significant portion of market volumes, reflecting the high level of activity by these traders.
Together, AMMs and CLOBs provide a robust, efficient, and diverse trading environment that caters to a broad spectrum of trading activities and preferences — from casual investors who benefit from the simplicity and liquidity of AMMs to professional traders who utilize the advanced functionalities and efficient price discovery of CLOBs. This symbiosis ensures that both market frameworks thrive, each playing a pivotal role in the DeFi landscape.




评论 (0)