Uniswap v4 introduces a new architecture for creating customizable hooks, providing developers with powerful tools to extend and enhance the functionality of the protocol. This tutorial will guide you through building Uniswap v4 hooks using the v4-template and leveraging ethui to streamline the development process. We'll cover setup, development, testing, and debugging through a technical walkthrough with practical examples.
Prerequisites
Before diving in, ensure you have the following:
-
Foundry: A powerful Ethereum development framework.
-
Anvil: A local EVM chain simulator.
-
ethui: A UI toolkit for Ethereum development.
Step 1: Setting Up the v4-template
-
Clone the v4-template Repository
git clone https://github.com/uniswapfoundation/v4-template.git cd v4-template -
Install Dependencies Ensure you have Foundry installed. Then, run:
forge install forge test -
Local Development with Anvil Start Anvil in a new terminal:
anvilIn another terminal, deploy the hooks on the local Anvil chain:
forge script script/Anvil.s.sol --rpc-url http://localhost:8545 --private-key 0xac0974bec39a17e36ba4a6b4d238ff944bacb478cbed5efcae784d7bf4f2ff80 --broadcast
Step 2: Developing a Hook
Let's create a hook that logs various events such as swaps and liquidity changes. We'll use the provided Counter.sol as a starting point.
-
Modify
Counter.solto Track Events// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT pragma solidity ^0.8.24; ... contract Counter is BaseHook { using PoolIdLibrary for PoolKey; mapping(PoolId => uint256) public beforeSwapCount; mapping(PoolId => uint256) public afterSwapCount; mapping(PoolId => uint256) public beforeAddLiquidityCount; mapping(PoolId => uint256) public beforeRemoveLiquidityCount; constructor(IPoolManager _poolManager) BaseHook(_poolManager) {} ... } -
Test the Hook Create a test file to validate the hook's functionality.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT pragma solidity ^0.8.24; ... contract CounterTest is Test, Deployers { using PoolIdLibrary for PoolKey; using CurrencyLibrary for Currency; Counter counter; PoolId poolId; function setUp() public { ... } function testCounterHooks() public { // positions were created in setup() assertEq(counter.beforeAddLiquidityCount(poolId), 3); assertEq(counter.beforeRemoveLiquidityCount(poolId), 0); assertEq(counter.beforeSwapCount(poolId), 0); assertEq(counter.afterSwapCount(poolId), 0); // Perform a test swap // bool zeroForOne = true; int256 amountSpecified = -1e18; // negative number indicates exact input swap! BalanceDelta swapDelta = swap(key, zeroForOne, amountSpecified, ZERO_BYTES); // ------------------- // assertEq(int256(swapDelta.amount0()), amountSpecified); assertEq(counter.beforeSwapCount(poolId), 1); assertEq(counter.afterSwapCount(poolId), 1); } } -
Run Tests
forge test
Step 3: Leveraging ethui for Debugging and Development
ethui is a developer's crypto wallet equipped with extensive tooling to speed up your Ethereum development workflows. Here's how to leverage ethui specifically for building hooks:
-
Install and Configure EthUI: Download and install the latest release of ethui from the releases page. ethui automatically detects and connects to your running Anvil instance on
http://localhost:8545. You can skip most of the onboarding steps (like setting up Alchemy.com) as they are primarily for mainnet usage.- Set Up ABI Monitoring Configure ethui to monitor your filesystem for foundry projects, indexing the output ABIs automatically.
-
Enable Foundry Integrations: ethui will automatically index ABIs for contracts within your Foundry project, making them readily available within the interface.
-
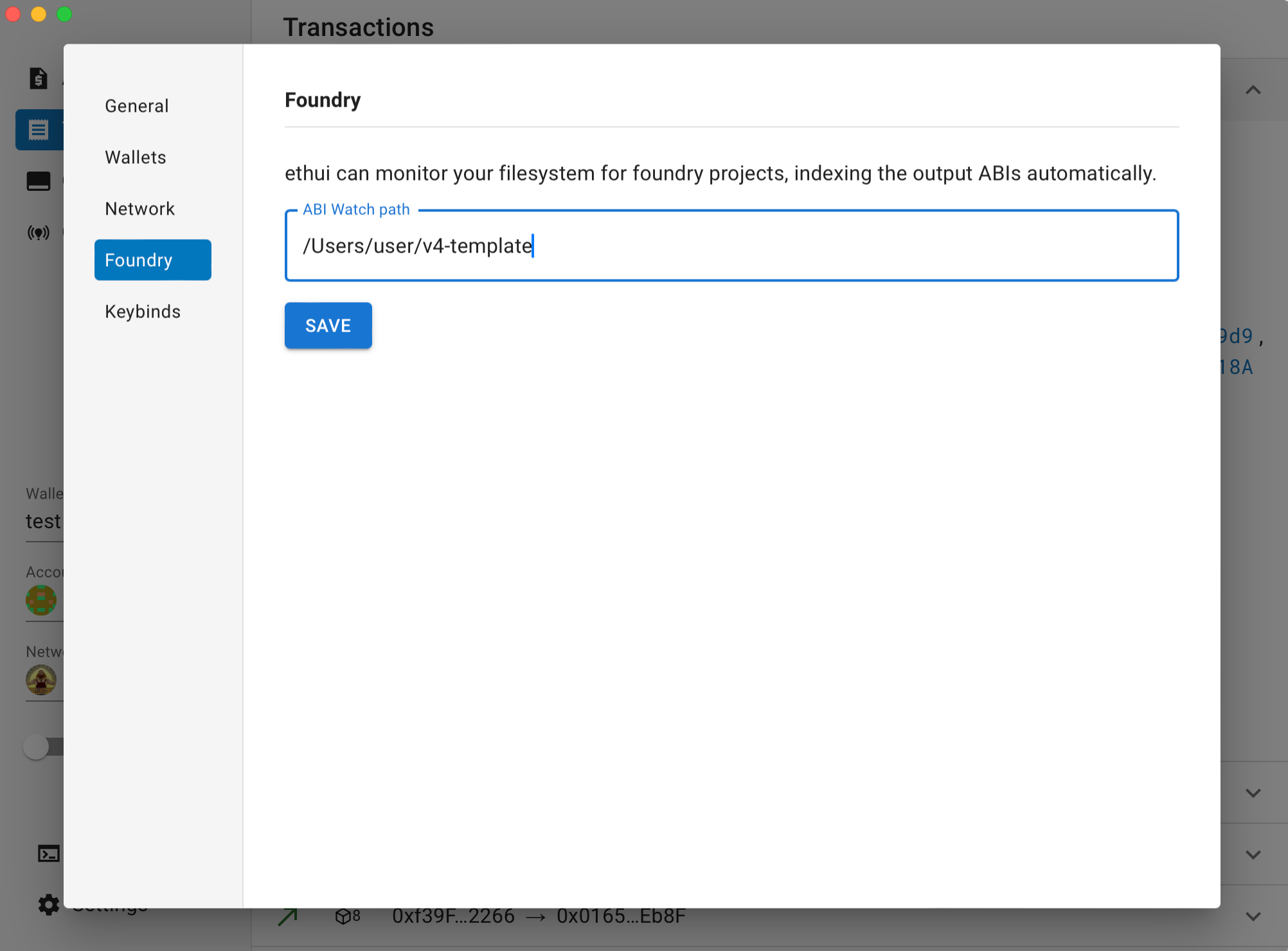
Navigate to Settings: Open ethui and navigate to the "Foundry" settings.
-
Set ABI Watch Path: Enter the path to your v4-template project directory. For example:
/Users/username/v4-template
-
-
Real-time Transaction Editing and Debugging: ethui provides a powerful transaction explorer that decodes calldata and displays human-readable information about your contract interactions:
-
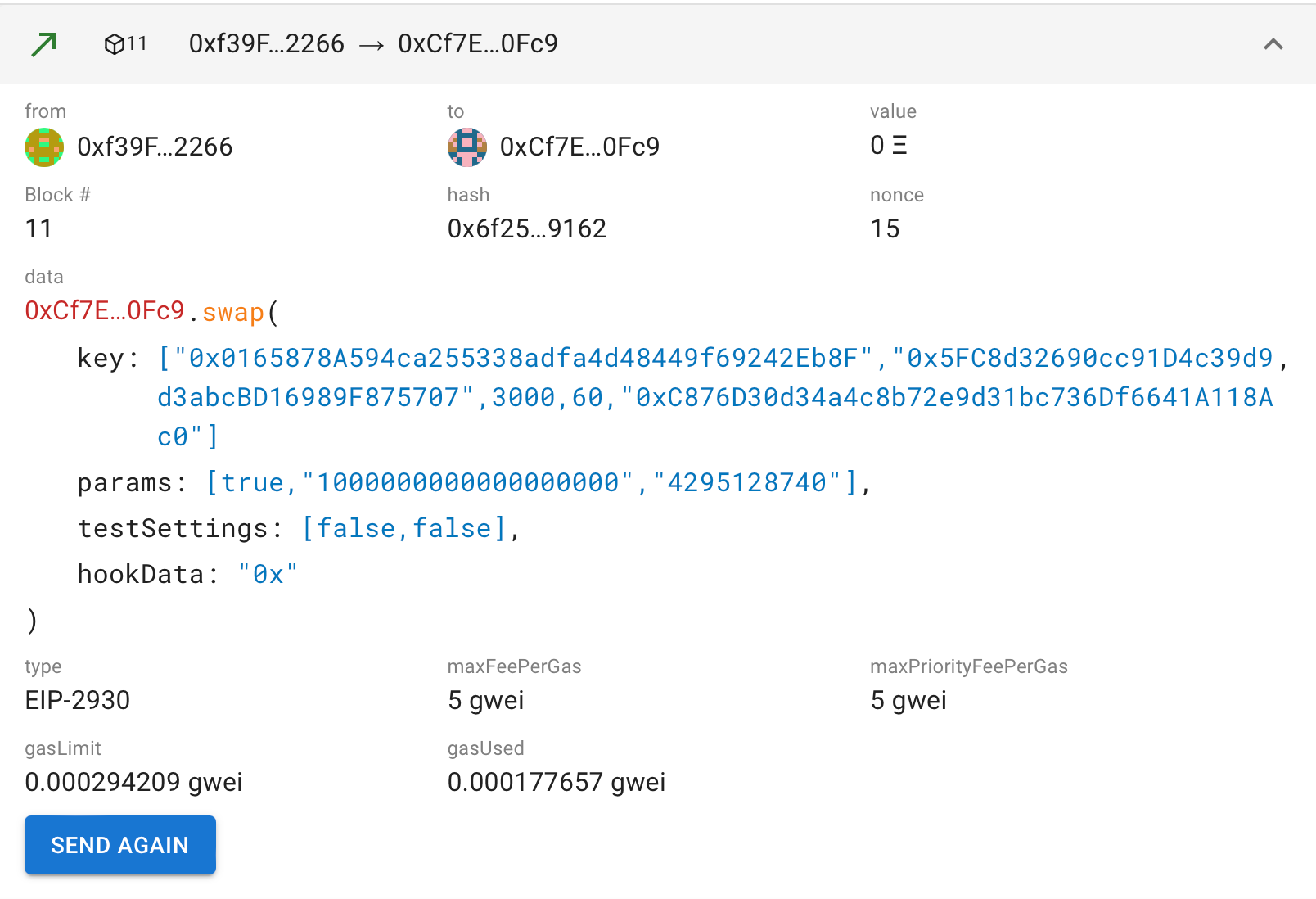
Open Transactions: Navigate to the "Transactions" tab in ethui. Each transaction related to your contracts will be listed.
-
View Decoded Data: Selecting a transaction reveals its details:
-
Function Call: Clearly see which function of your contract was invoked (e.g.,
swap,addLiquidity). -
Decoded Parameters: ethui automatically decodes calldata, showing the exact values passed to your hook functions, significantly simplifying the debugging process.
-
-
-
-
Transaction Simulation & Replay: ethui empowers you to test your hooks under various conditions without redeploying contracts:
-
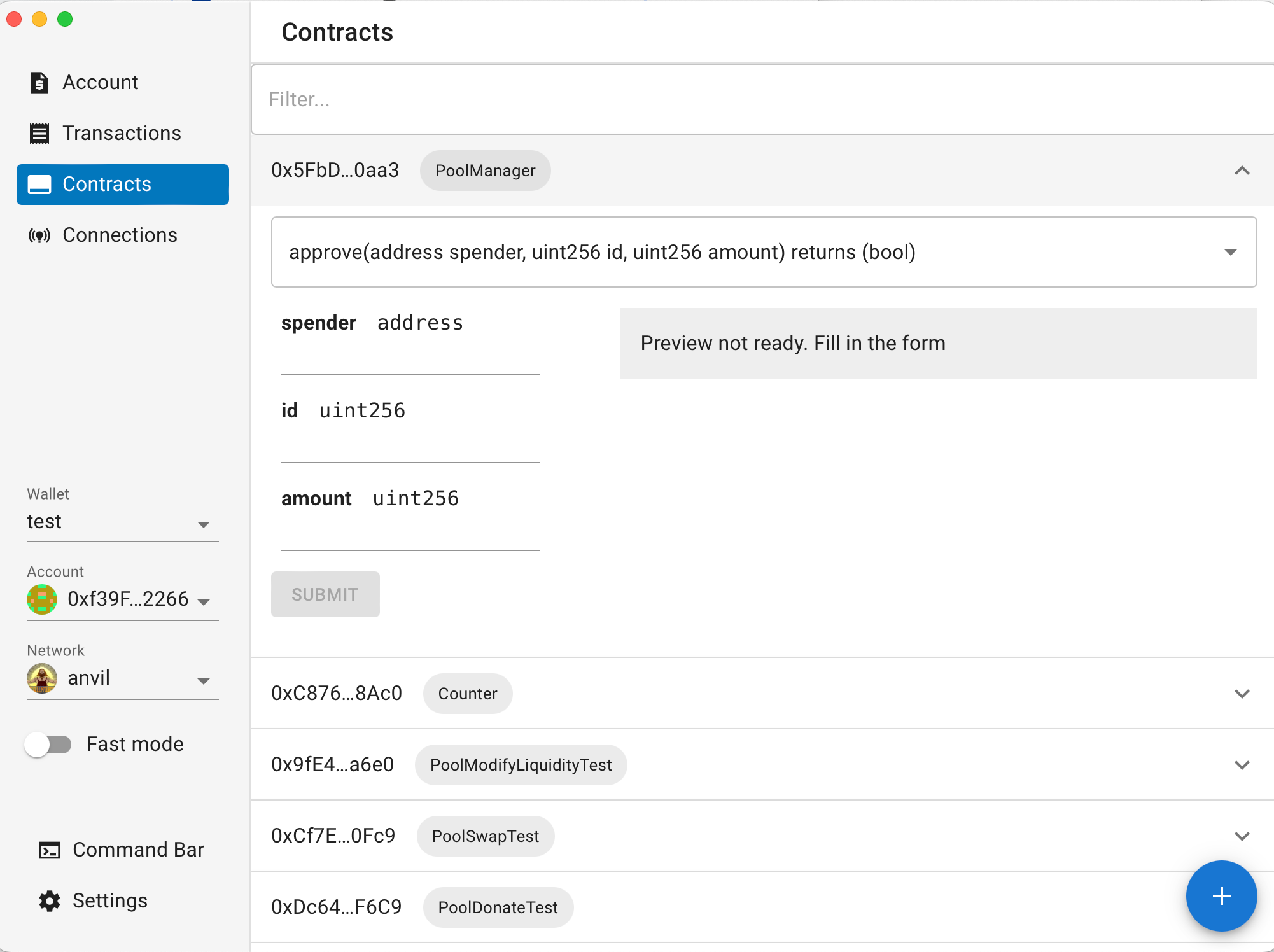
Navigate to Contracts: Go to the "Contracts" tab, where your indexed Foundry contracts appear.
-
Select Your Hook Contract: Choose your deployed hook contract (e.g.,
Counter). -
Simulate Transactions: The interface provides a user-friendly way to interact with your contract:
-
Select Function: Choose the specific hook function you want to test.
-
Input Parameters: Provide different input values to your hook function, simulating various scenarios.
-
Execute Simulation: ethui executes the transaction against your local Anvil instance, displaying the results. This enables you to rapidly iterate and test your hook logic.
-
-
Advanced Debugging with ethui
ethui goes beyond basic debugging:
-
Edit & Replay Transactions: The "Send Again" button in the Transaction tab allows you to modify transaction parameters and resend, enabling you to quickly test different scenarios or fix bugs in your hook logic without redeploying.
-
Multiple Wallet Management: Easily manage multiple wallets within ethui. This is useful for simulating interactions from different addresses (e.g., liquidity providers, swappers) when testing your hooks.
Example: Debugging a Swap Event with ethui
Let's say your Counter hook isn't correctly incrementing the afterSwapCount. Here's how ethui helps:
-
Trigger a Swap: Initiate a swap transaction that should invoke your hook, either programmatically or using the ethui interface.
-
Inspect the Transaction: In ethui's Transactions tab, find the swap transaction.
-
Verify Hook Execution: Examine the decoded transaction data. You should see a call to your hook contract's functions (e.g.,
beforeSwap,afterSwap). -
Inspect State Changes: Open your
Countercontract in the "Contracts" tab and read the value ofafterSwapCountfor the relevant pool. If it's not incrementing, you've isolated the problem area in your hook's logic. -
Debug with Simulations: Use ethui's transaction simulation to call the problematic hook function directly with various inputs. This iterative process helps pinpoint the logic flaw in your code.
By combining the v4-template and ethui, you can efficiently develop, test, and debug custom hooks for Uniswap v4. This setup not only accelerates the development process but also provides robust tools for ensuring the reliability and security of your hooks.
For more advanced hook implementations and examples, refer to the v4-periphery repository and v4-by-example.
We encourage you to report any bugs or suggestions for ethui. You can do this through GitHub issues or by reaching out directly to naps62 on telegram!
Happy coding! 🦄




评论 (0)