Introduction
Welcome, developers, to the next frontier in decentralized finance (DeFi). Ensuring the stability and security of DeFi platforms is paramount, particularly when managing collateralized positions. In this blog, we will explore how to leverage Actively Validated Services (AVS) and EigenLayer to create decentralized, efficient, and cost-effective liquidation mechanisms.
This approach addresses existing challenges and enhances the reliability of DeFi ecosystems.
The Need for Robust Liquidation Mechanisms
Understanding the Current Landscape
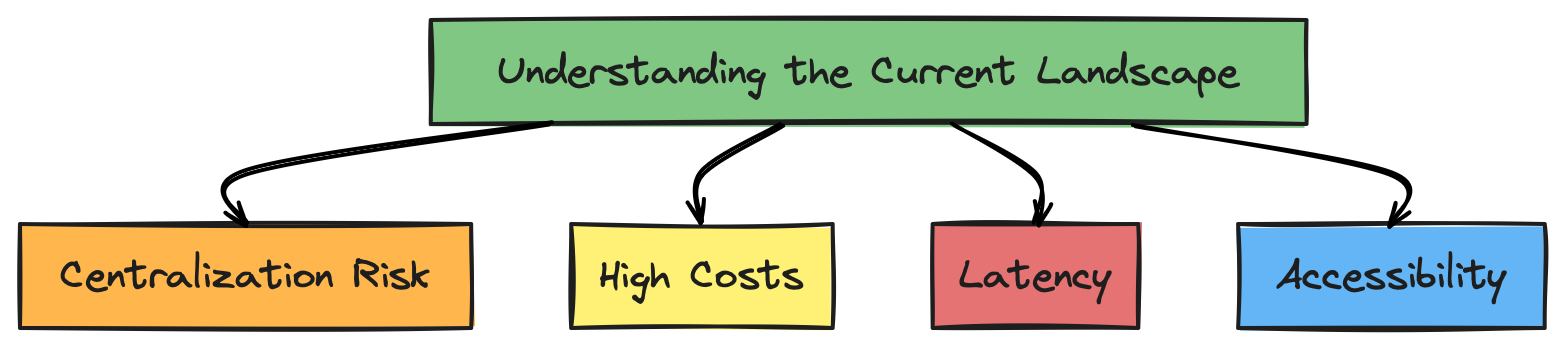
DeFi has unlocked unprecedented financial innovation, allowing users to borrow, lend, and trade assets in a decentralized manner. However, the backbone of these services is the ability to manage and liquidate collateralized positions to maintain system stability.
Traditional liquidation mechanisms face several significant issues:
-
Centralization Risk: Relying on centralized liquidators introduces single points of failure and potential market manipulation.
-
High Costs: Decentralized liquidations can incur high gas fees and require rapid execution.
-
Latency: Delays in liquidating under-collateralized positions can lead to systemic risks and losses.
-
Accessibility: Smaller DeFi projects may struggle to implement robust liquidation mechanisms due to resource constraints.
Complications in Existing Systems
The current mechanisms often fail to provide a seamless, secure, and cost-effective solution. Centralized actors dominate the space, and the lack of efficient decentralized alternatives puts the entire DeFi ecosystem at risk. Addressing these issues is crucial for the continued growth and stability of DeFi platforms.
Leveraging EigenLayer and AVS for Liquidation Mechanisms
Leveraging EigenLayer's Capabilities
EigenLayer introduces the concept of restaking, allowing existing Ethereum validators to secure additional decentralized applications (dapps) and infrastructure. By using the security and economic incentives of EigenLayer, we can create a decentralized network to manage liquidations more effectively.
Utilizing Actively Validated Services (AVS)
Actively Validated Services (AVS) are critical to implementing decentralized and robust services on top of EigenLayer. They allow developers to build services that leverage the pooled security of restaked ETH.
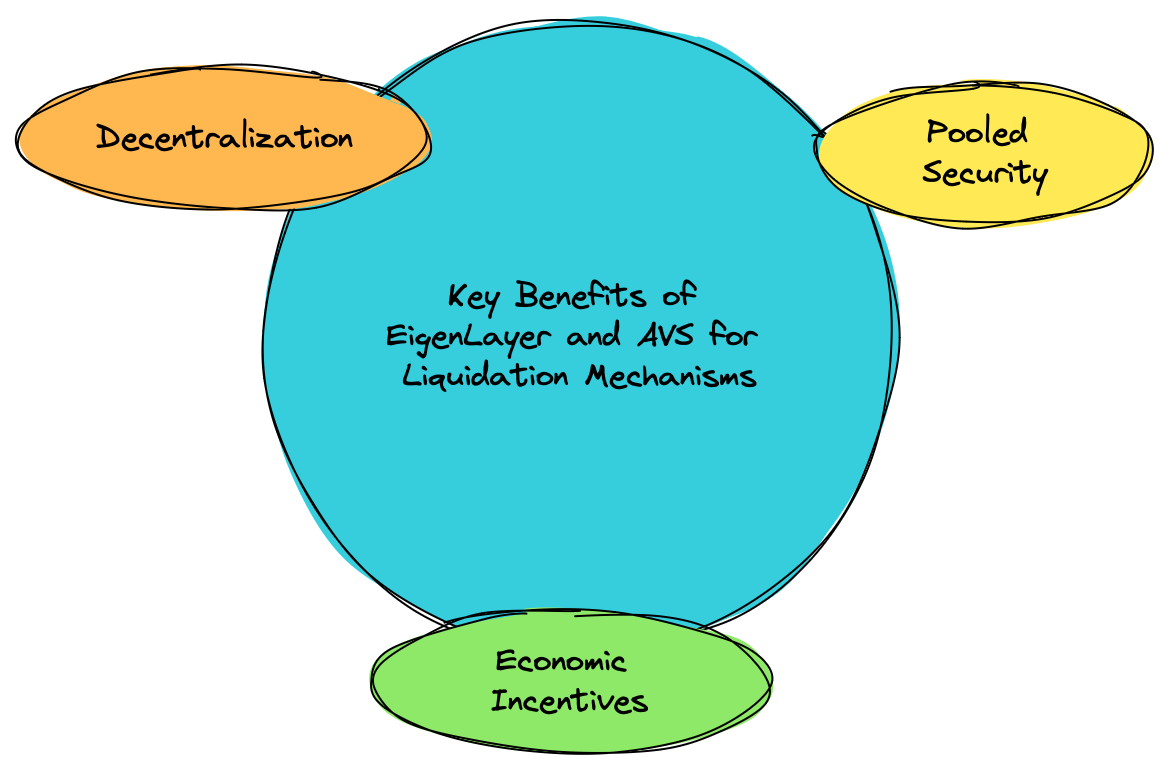
Key Benefits of EigenLayer and AVS for Liquidation Mechanisms
-
Pooled Security: Utilize Ethereum’s extensive validator network for enhanced security.
-
Economic Incentives: Offer additional rewards for validators participating in liquidation activities.
-
Decentralization: Reduce reliance on centralized entities and improve system resilience.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide for Decentralized Liquidation Nodes
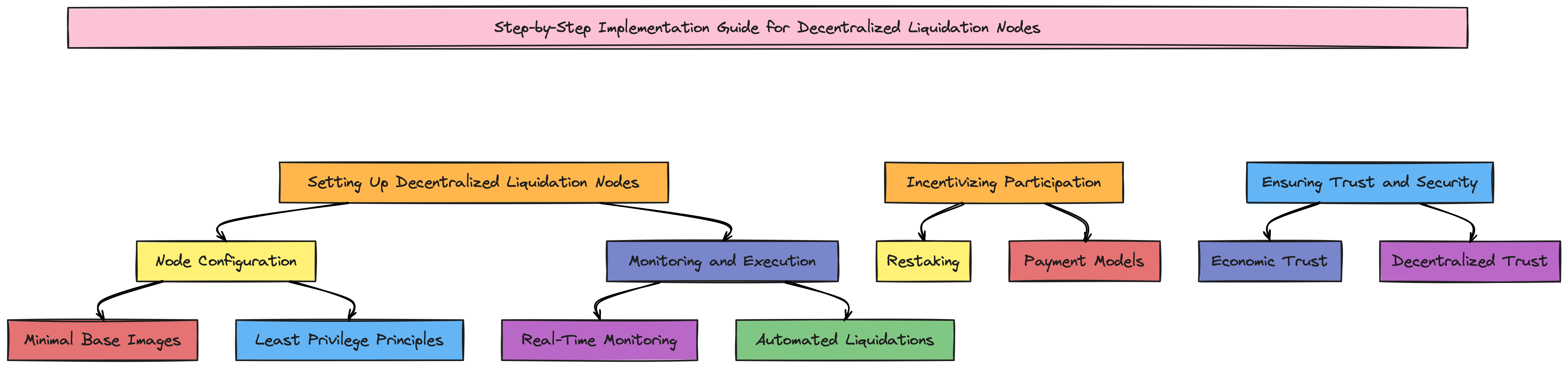
Setting Up Decentralized Liquidation Nodes
Liquidation nodes continuously monitor collateralized positions and execute liquidations when necessary. Here's how to set them up:
Node Configuration:
-
Minimal Base Images: Use minimal base images for nodes to reduce vulnerabilities.
-
Least Privilege Principles: Ensure nodes operate with the least necessary privileges to enhance security.
Monitoring and Execution:
-
Real-Time Monitoring: Implement tools for continuous tracking of collateralized positions. Data tools can help visualize data and handle real-time alerts.
-
Automated Liquidations: Develop smart contracts that automatically trigger liquidations when thresholds are breached. Consider using tools like Chainlink Keepers for automation.
Incentivizing Participation
To ensure active participation and high-quality liquidations, nodes must be properly incentivized. Here are some strategies:
Restaking:
- Allow existing Ethereum validators to restake their ETH to secure the liquidation network, earning additional rewards.
Payment Models:
- Implement dual staking mechanisms where nodes earn fees in ETH or native tokens. This approach encourages participation by offering multiple avenues for rewards.
Ensuring Trust and Security
EigenLayer’s economic and decentralized trust ensures the integrity and reliability of the liquidation processes. Here’s how to implement it:
Economic Trust:
- Use slashing mechanisms to penalize nodes that fail to perform or act maliciously. Ensure these mechanisms are clearly defined and enforceable through smart contracts.
Decentralized Trust:
- Ensure a broad and geographically dispersed set of nodes to prevent collusion and enhance security. This can be achieved by encouraging participation from diverse validators across different regions.
Combining Automated and Manual Oversight
Automated Liquidations
Automated systems can handle most liquidation processes efficiently. Here’s how to set it up:
Smart Contracts:
- Develop smart contracts to monitor positions and trigger liquidations automatically. Use platforms like Hardhat or Truffle to build and test these contracts.
Real-Time Data Feeds:
- Integrate with decentralized oracles like Chainlink to get real-time data feeds for accurate monitoring of collateral values.
Manual Oversight
For complex scenarios or where automated systems fail, manual oversight by experienced liquidators ensures comprehensive coverage. Here’s how to integrate manual oversight:
Human Auditors:
- Establish a network of experienced auditors who can review automated reports and intervene when necessary. This hybrid approach combines the speed of automation with the expertise of human auditors.
Emergency Protocols:
- Implement emergency protocols to allow human auditors to take over in case of critical failures or unexpected events.
Continuous Improvement Through Governance
Decentralized Governance Model
Implement a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) to manage updates to liquidation standards and incentivize community contributions. Here’s how to do it:
DAO Setup:
- Use platforms like Aragon to set up the governance structure. Ensure it is inclusive and allows for community participation in decision-making.
Incentives for Contributions:
- Provide incentives for community members to contribute to the development and improvement of liquidation protocols. This could be in the form of token rewards or recognition within the community.
Regular Updates and Audits
Maintain an evolving set of best practices and operational standards. Here’s how to ensure continuous improvement:
Regular Audits:
- Conduct regular security audits of the smart contracts and systems. Engage with reputable audit firms and consider bug bounty programs to identify vulnerabilities.
Feedback Loops:
- Establish feedback loops with users and operators to gather insights and make necessary adjustments. Use platforms like Discord or Telegram for community engagement and feedback collection.
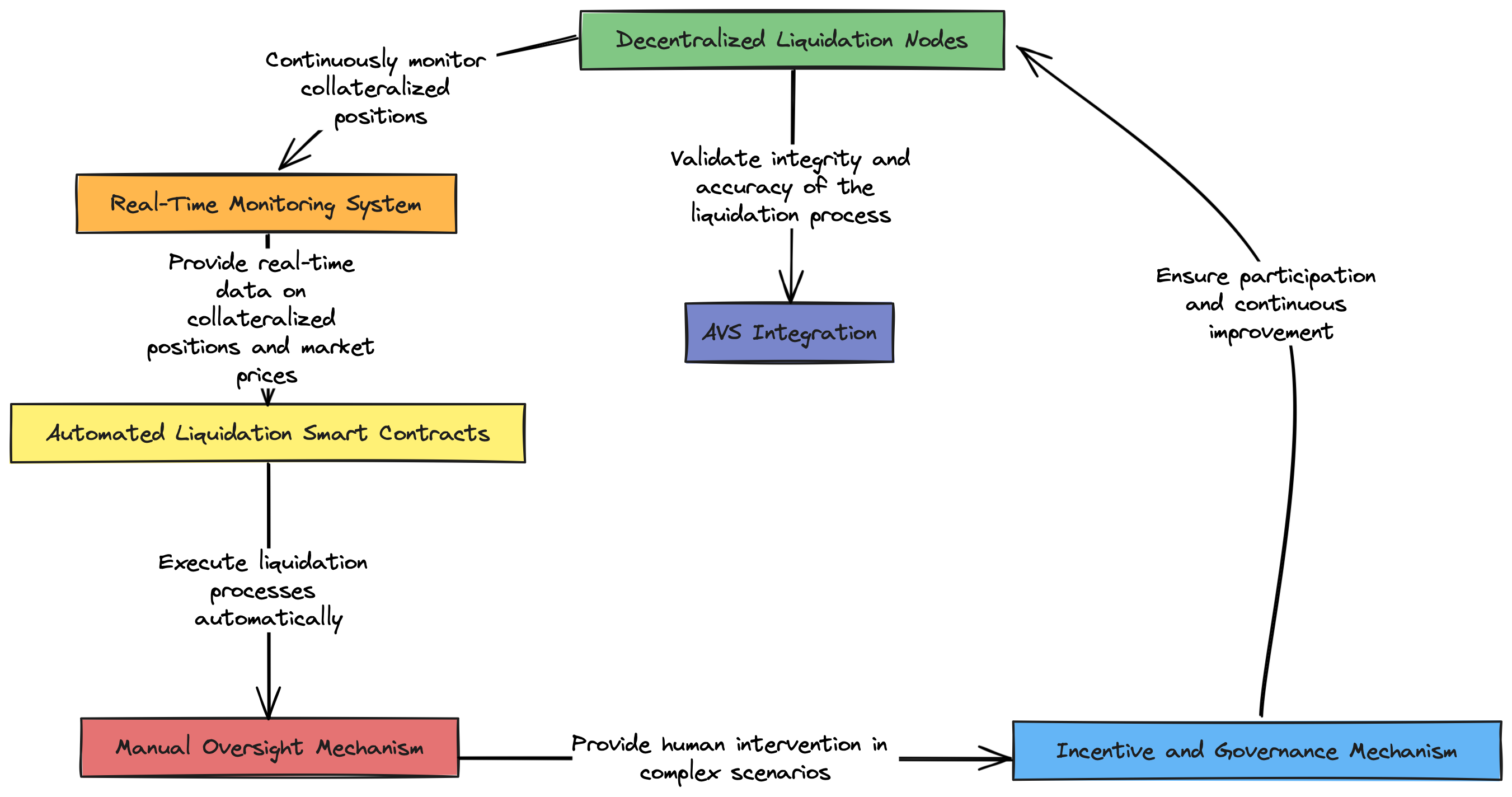
Suggested Architecture for Decentralized Liquidation Mechanism
Overview
The architecture consists of the following main components:
-
Decentralized Liquidation Nodes
-
Real-Time Monitoring System
-
Automated Liquidation Smart Contracts
-
Manual Oversight Mechanism
-
Incentive and Governance Mechanism
Detailed Architecture
1. Decentralized Liquidation Nodes
Role: Continuously monitor collateralized positions and execute liquidations.
-
Node Setup: Nodes are operated by validators who restake their ETH through EigenLayer. These nodes run minimal base images and follow least privilege principles for enhanced security.
-
Communication Protocol: Nodes use a decentralized communication protocol like libp2p to share information and coordinate actions.
AVS Integration:
- Actively Validated Services: Nodes use AVS to validate the integrity and accuracy of the liquidation process. This ensures that liquidations are conducted fairly and transparently.
2. Real-Time Monitoring System
Role: Provides real-time data on collateralized positions and market prices.
-
Data Feeds: Integrate with decentralized oracles (e.g., Chainlink) to fetch real-time data on asset prices and collateralization levels.
-
Monitoring Tools: Use tools for data collection and for visualization and alerting.
Flow:
-
Data Collection: Nodes continuously collect data from oracles about collateralized positions.
-
Data Analysis: The monitoring system analyzes the data to identify under-collateralized positions.
-
Alert Generation: Alerts are generated for positions that need liquidation, and the information is relayed to the liquidation nodes.
3. Automated Liquidation Smart Contracts
Role: Execute liquidation processes automatically when conditions are met.
-
Smart Contracts: Developed using Solidity, deployed on your preferred blockchain.
-
Automation Tools: Use Chainlink Keepers for automation of contract execution.
Flow:
-
Trigger Conditions: Smart contracts are programmed with conditions for triggering liquidations (e.g., collateralization ratio falls below a threshold).
-
Execution: When conditions are met, the contract executes the liquidation process, selling the collateral to repay the debt.
4. Manual Oversight Mechanism
Role: Provide human intervention in complex scenarios where automated systems may fail.
-
Human Auditors: A network of experienced auditors who can review and intervene in liquidation processes.
-
Emergency Protocols: Procedures for manual intervention in case of critical failures or unexpected events.
Flow:
-
Review Alerts: Human auditors review alerts generated by the monitoring system.
-
Manual Liquidation: If necessary, auditors can manually execute liquidations by interacting with smart contracts or directly with the liquidation nodes.
5. Incentive and Governance Mechanism
Role: Ensure participation and continuous improvement through economic incentives and decentralized governance.
-
Incentives: Provide rewards for validators and auditors based on their participation and performance.
-
Governance: Use a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) to manage updates and improvements.
Flow:
-
Restaking: Validators restake their ETH to participate in the liquidation network.
-
Rewards Distribution: Validators and auditors receive rewards for their contributions, distributed through smart contracts.
-
Governance Decisions: Community members participate in governance decisions through the DAO, proposing and voting on updates and improvements.
Conclusion
By leveraging AVS and EigenLayer, we can transform liquidation mechanisms into a decentralized, efficient, and cost-effective service. This innovative approach not only addresses the scalability, cost, and security challenges of traditional systems but also fosters a more stable and trustworthy DeFi ecosystem.
Implementing these advanced strategies will enable you to build robust, secure, and resilient DeFi platforms, ensuring long-term stability and growth.
Happy coding and secure liquidations!



评论 (0)