The internet has undergone a remarkable transformation since its inception, evolving through various phases that have fundamentally changed how we interact with digital information. From the early days of static web pages to the dynamic and interactive platforms of Web 2.0, the internet has continuously reinvented itself.
In 1991, The first website in history was created. You can still view it online.
Now, we stand on the brink of a new era: Web3. This article explores the evolution of the internet, focusing on the revolutionary potential of Web3.
The Dawn of the Internet 🌅: Web 1.0
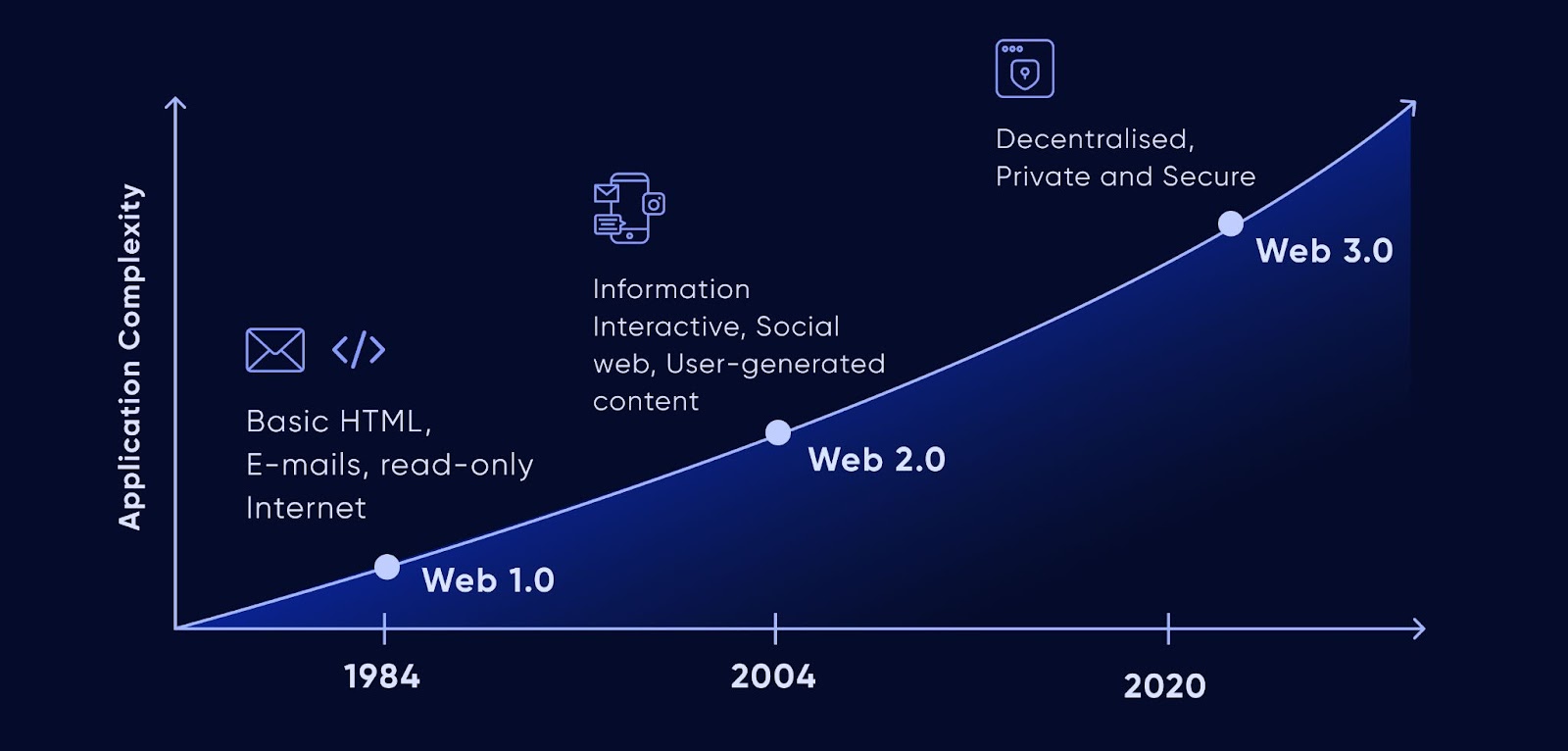
Web 1.0, often referred to as the "Static Web," was the internet's first phase, spanning from the early 1990s to the early 2000s. This era was characterized by static web pages, basic HTML, and limited user interaction. Websites were essentially digital brochures, providing information without much interactivity.
The primary goal was to publish and access information. Search engines like Yahoo and early versions of Google emerged to help users navigate this vast digital landscape.
The Rise of Interactivity🌐: Web 2.0
The transition to Web 2.0, known as the "Dynamic Web," began in the early 2000s. This phase introduced interactive and user-generated content, transforming the internet into a more participatory and social platform.
Key features of Web 2.0 included:
-
🔔Social Media Platforms: Websites like Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube allowed users to create, share, and interact with content on an unprecedented scale.
-
📱Dynamic Web Applications: AJAX and other technologies enabled real-time updates and seamless user experiences.
-
💻 E-commerce: Online shopping became more sophisticated with platforms like Amazon and eBay, offering personalized recommendations and user reviews. 🛒
Web 2.0 democratized content creation, making the internet more engaging and collaborative. However, it also gave rise to new challenges, such as data privacy concerns and the concentration of power in the hands of a few tech giants. 🏢
The Seeds of Web3: Blockchain Technology 🌱
The foundation for Web3 was laid in 1991 when scientists W. Scott Stornetta and Stuart Haber introduced the first blockchain project to timestamp digital documents. However, the concept didn't gain significant traction until the launch of Bitcoin in 2009.
Created by the pseudonymous inventor Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin introduced a decentralized digital currency based on blockchain technology.
💡 A blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring transparency and security.
In the Bitcoin network, "miners" validate transactions by solving complex mathematical problems, adding new blocks of data to the chain, and earning newly created bitcoins as a reward.
In 2015, Ethereum was launched with the perspective of "one computer for the entire planet." Ethereum is both a digital currency and a platform for building decentralized applications (dApps). Ethereum's blockchain can store not only transaction data but also smart contracts or self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code.
📝 Ethereum's flexibility opened up new possibilities for blockchain technology. This marked the beginning of Web3's potential as a decentralized web. 🚀
Understanding Web3: The Decentralized Web 🌍
Web3 represents the next evolution of the internet, characterized by decentralization, transparency, and user empowerment. It leverages blockchain technology to create a web where users have more control over their data and online interactions.
In short, this evolution can be explained as:
https://x.com/himgajria/status/1266415636789334016
Key features of Web3 include:
-
✅ Decentralization: Web3 operates on permissionless blockchains, eliminating the need for centralized authorities. This ensures that no single entity has control over the network.
-
✅ Trust less: Web3 is based on open-source software, allowing participants to interact directly without relying on a trusted intermediary. This means transactions and interactions can occur without the need for middlemen, enhancing security and efficiency.
-
✅ Permissionless: Anyone can participate in the Web3 ecosystem without needing authorization from a governing body. This open access promotes inclusivity and democratizes the internet, enabling more people to engage with and benefit from decentralized applications.
-
✅ Tokenization: Cryptocurrencies and tokens are used to incentivize network participants, enabling new economic models and shared ownership. 💰 Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts automate agreements and transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries.
-
✅ Privacy and Security: Transactions on Web3 are transparent yet secure, with users identified by cryptographic addresses rather than personal information.
-
✅ Decentralized Applications (dApps): Web3 applications run on blockchains, decentralized peer-to-peer networks, or a combination of both. These decentralized apps, known as dApps, leverage the distributed nature of blockchain technology to provide more secure and resilient services. 💻
The Impact of Web3 🌟
Web3 has the potential to revolutionize various industries by addressing some of the core issues of Web 2.0. For example:
-
👉 Finance: Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms enable peer-to-peer lending, borrowing, and trading without traditional banks.
-
👉 Content Creation: Creators can monetize their work directly through NFTs (non-fungible tokens) and decentralized platforms, reducing reliance on intermediaries.
-
👉 Data Ownership: Users regain control over their data, deciding how and when it is shared. 🗃️
The evolution of the internet from Web 1.0 to Web3 is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of innovation. While Web 2.0 transformed the internet into a dynamic and interactive space, it also highlighted the need for greater user control and decentralization. Web3 promises to address these challenges, ushering in a new era of the internet.
⚠️ Note: I have created this blog from my understanding and learning at #BRBBootcamp by Push Builders.




评论 (0)