Welcome to this blog ✍️ !! Let’s learn about Gas Optimization Techniques in EVM-based Smart Contracts. ⤵️
What is Gas?
In the Ethereum network, "gas" refers to the unit that measures the amount of computational effort required to perform operations, such as executing a smart contract or performing a transaction.
Gas is fundamental to the functioning of the Ethereum blockchain, ensuring that resources are allocated fairly and that the network remains secure and efficient.
Why is Gas Necessary in Ethereum❗?
The gas serves several crucial purposes in the Ethereum ecosystem:
-
Resource Management: Gas limits the number of computational steps a transaction can execute, preventing any single transaction from monopolizing network resources.
-
Security: By requiring gas fees, Ethereum mitigates the risk of denial-of-service attacks, as attackers would need to spend significant amounts of ether to overwhelm the network.
-
Incentive Alignment: Gas fees incentivize miners to validate and include transactions in the blockchain, ensuring the network remains decentralized and operational.
Ethereum Gas Mechanism⚙️
The Ethereum gas mechanism operates on a simple principle: users specify a gas limit and a gas price for their transactions.
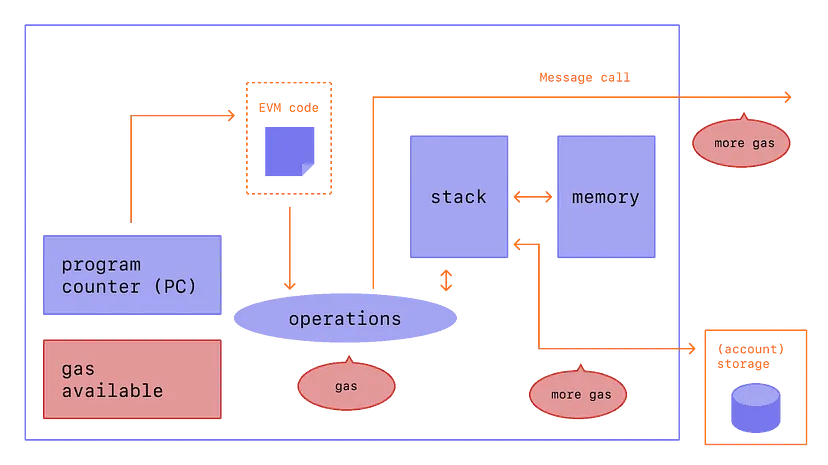
The gas limit is the maximum amount of gas the user is willing to consume, while the gas price is the amount of ether the user is willing to pay per unit of gas. The total fee is the product of the gas used and the gas price.
-
Gas Limit: This is the maximum amount of gas you are willing to spend on a transaction. If the gas consumed by the transaction exceeds this limit, the transaction fails.
-
Gas Price: This is the amount of ether you're willing to pay per unit of gas. Higher gas prices can incentivize miners to prioritize your transaction.
Best Optimization Techniques⚡for Reducing Gas
Optimizing gas consumption is critical for developers looking to deploy efficient and cost-effective smart contracts. Here are some of the best practices:
-
Minimize Storage Operations: Storage operations (SSTORE and SLOAD) are among the most gas-intensive. Reducing the number of storage writes and reads can significantly lower gas costs.
-
Use Bitwise Operations: Bitwise operations are cheaper than arithmetic operations. Using them for certain calculations can save gas.
-
Optimize Loops: Ensure loops have a fixed upper bound and avoid unbounded loops. This prevents excessive gas consumption and potential out-of-gas errors.
-
Batch Operations: Batch multiple transactions into a single transaction when possible to reduce overall gas consumption.
-
Use the Latest Solidity Version: Newer versions of Solidity often come with optimizations and improvements that can help reduce gas costs.
Short Tips to Follow👇
-
Avoid Unnecessary Computations: Perform as many computations off-chain as possible to save on gas.
-
Leverage Immutable Variables: Immutable variables are set once and cannot be changed, saving gas compared to mutable storage variables.
-
Use Libraries Wisely: Libraries can reduce bytecode size, but excessive use can increase gas costs. Balance their use to optimize gas consumption.
-
Optimize Data Structures: Use more gas-efficient data structures, such as mappings instead of arrays, when appropriate.
-
Consider Gas Tokens: Gas tokens can help reduce gas costs during periods of high network congestion by leveraging storage refunds.
Optimizing gas in Ethereum smart contracts is not just about reducing costs; it also enhances the efficiency and performance of the blockchain.
By following best practices and leveraging the latest tools and techniques, developers can create more robust and cost-effective smart contracts.
⚠️ Note: I have created this blog from my understanding and learning at #BRBBootcamp by Push Builders.




评论 (0)