Since the beginning of 2023, there has been talk of the potential for integrating blockchain technology and AI, probably becoming the most hyped trend together with RWA.
It is within this context that Bittensor emerges, founded on the idea of leveraging the potential of blockchain technology for the benefit of artificial intelligence.
Bittensor is an highly interesting project that offers a glimpse into the future of these two technologies, and we have decided to delve deeper into this vision.
The Evolution of AI
Our journey begins in the mid-20th century, with AI being merely a whisper among mathematicians and philosophers contemplating the potential of machines thinking like humans. It's challenging to succinctly describe the complex path that has since transformed it into a fundamental reality of modern technology, but we will try to highlight what seem to be the most important milestones:
-
1950 - The Turing Test: Alan Turing proposes a test as a criterion for evaluating a machine's intelligence, laying the groundwork for the concept of artificial intelligence.
-
1956 - The birth of AI: The Dartmouth conference takes place, marking the beginning of research aimed at understanding how human brain learning works in order to create a machine capable of learning in the same way. The document proposing the conference, presented in 1955, introduces the term "artificial intelligence" for the first time.
-
1966 - ELIZA: Joseph Weizenbaum creates ELIZA, one of the first programs capable of simulating a conversation through natural language processing.
-
1980 - Expert systems: These are systems capable of solving problems within a limited domain but with performance similar to that of a human expert in the same domain. The first Expert System was developed in 1965, but the rise of these programs occurred in the '80s, leading to increased investment in research.
-
1986 - The Backpropagation Algorithm: The rediscovery of the backpropagation algorithm, originally proposed in 1969, provided new momentum for neural network research.
-
1997 - Deep Blue: IBM Deep Blue defeats world chess champion Garry Kasparov, demonstrating machines' capability to outperform humans in highly strategic tasks.
-
2012 - AlexNet: AlexNet, a neural network model, wins the ImageNet competition, marking a turning point for the effectiveness of deep learning in automatic image recognition.
-
2016 - AlphaGo: DeepMind's AlphaGo, a software created to play Go, defeats one of the world's strongest Go players, Lee Sedol.
-
2020 - GPT-3: OpenAI launches GPT-3, a generative language model capable of writing surprisingly coherent texts and even programming code.
From this point on, it's hard not to be aware of the developments.
Today, AI is applied in numerous sectors, radically transforming processes and positioning itself as one of the most revolutionary technologies on the market.
Refusing to understand how it can be used, diverting attention from the problems that still need to be solved for it to continue improving, or, more generally, adopting a hostile attitude towards it, can only result in a rejection of the looming future, with all its consequences.
Blockchain meets AI
In recent developments, two technologies, AI and blockchain, have emerged as major forces, capturing the attention of both industry experts and the wider market. Their vast application potential has spurred increased interest and investigation into how they might reshape various sectors.
At that point, the question naturally arose: what if we could use the trustless and transparent nature of blockchain to solve some of AI's most urgent challenges, such as data privacy, security, and accessibility?
This curiosity sparked a new wave of innovation, and several projects emerged as a result, aiming to understand how decentralized networks could host AI operations and encourage contributions and collaborations in previously unimaginable ways.
By merging the decentralization and security of blockchain with the intelligence and adaptability of AI, we are entering a new frontier where the collective potential of these technologies can be harnessed for the benefit of both.
With these premises, the importance of Bittensor becomes clear as it paves the way for a new paradigm in which AI can grow and thrive within a decentralized and collaborative ecosystem. This approach addresses some of the traditional barriers in AI development, such as data silos and the monopolization of computing resources, and opens new avenues for innovation, where anyone, anywhere, can both contribute to and benefit from AI.
Bittensor
Bittensor is an innovative protocol for creating decentralized subnets (like Avalanche), aimed at producing and enhancing artificial intelligence through incentive-based competition mechanisms.
Each subnet within the Bittensor ecosystem acts as an autonomous competitive market, where participants, "subnet miners" and "subnet validators," collaborate and compete to generate the best AI responses, receiving rewards in the form of the native token $TAO in return.
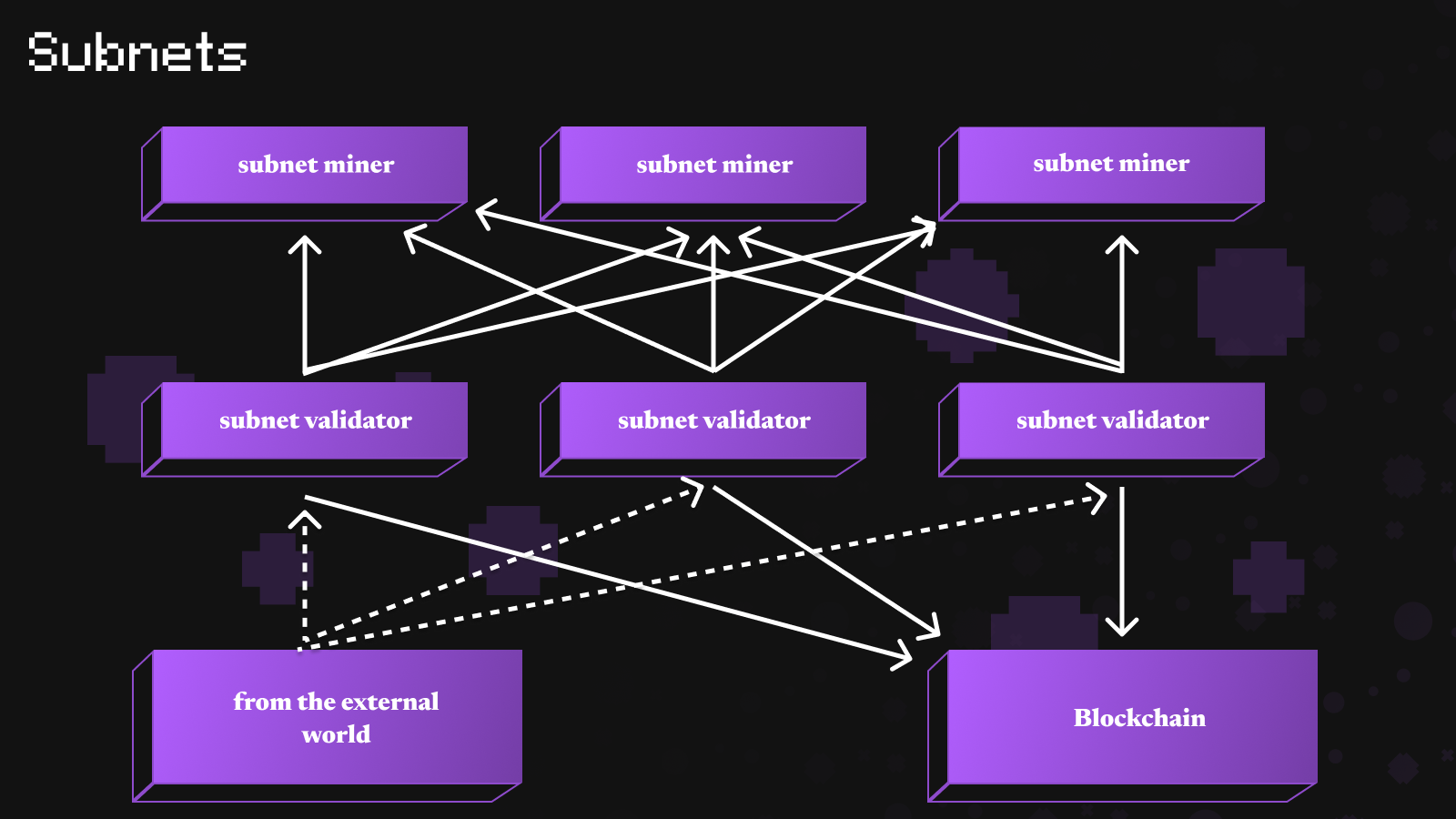
The network operates as an open peer-to-peer ecosystem, allowing for the sharing, training, and trading of AI and ML models, promoting a global ecosystem where AI models come together to form a decentralized network acting as a "global brain," with each node or "neuron" representing a distinct machine learning model. These models collaborate through the network, processing information and providing intelligent responses.
The platform is based on a proprietary blockchain integrated through a Bittensor API that connects all the essential elements of the ecosystem and is designed to allow subnet owners to write their own incentivization mechanisms. This enables the decentralization of governance across multiple stakeholders.
To reward miners and validators, Bittensor uses the Yuma consensus mechanism: validators judge the work of miners by assigning them scores, or "weights," based on how quickly and intelligently they respond to requests. These scores are then compiled into a large list, called a weight matrix, which helps to determine who is doing the best job. Yuma ensures that validators who agree with the common judgment receive a reward, thus encouraging honesty and supporting quality evaluations.
TaoPad: A DeFi Protocol for $TAO
The next step was to consider how the native token of the Bittensor network ($TAO) could be enhanced in value by promoting interest and participation in decentralized AI among DeFi enthusiasts. As an answer to this question, TaoPad was born, a DeFi protocol that operates with $TAO.
Let's now look at the features of TaoPad.
With 35 subnets deployed in the mainnet, TaoPad is a dense interoperable ecosystem.

Mission: TaoPad's mission is to expand the Tao ecosystem to other networks to drive the value of the Tao token. This will be achieved through initiatives that benefit the BitTensor network and smart contracts designed to distribute rewards to TaoPad holders such as Wrapped Tao ($wTAO). TaoPad aims to become the reference point for all actors in the Tao ecosystem by acting as a gateway to the BitTensor network from Ethereum and allowing $TPAD holders to leverage the ongoing value accumulation on the BitTensor network, facilitating activities on the BitTensor network, and distributing acquired rewards to $TPAD holders.
Tokenomics: TaoPad has a total supply of one million tokens, $TPAD, with a circulating supply of 650,808 $TPAD tokens. Every purchase and sale transaction of $TPAD incurs a 5% fee, part of which is redistributed to $TPAD holders in the form of $wTAO on Arbitrum, while the rest is used according to community vote.
Bridge: Uses Layer Zero infrastructure, allowing $wTAO to expand onto new chains, starting with Arbitrum.
Launchpad: Enables new projects and teams to launch their ideas, prioritizing projects that aim to expand decentralized AI.
Community: TaoPad aims to place its community at the center of its ecosystem with the intent of promoting a supportive, engaging, and collectively growing environment. Through decentralized governance, it values the active contribution of its members through voting mechanisms and incentive programs.
Conclusion
Bittensor offers the possibility of generating value through the implementation and innovation of artificial intelligence. In doing so, it provides a huge incentive for the development of such technology and, at the same time, allows anyone interested in participating the opportunity to contribute to this development through a decentralized network that leverages blockchain as support.
TaoPad further incentivizes this ecosystem, a DeFi protocol based on Bittensor's native token ($TAO), allowing it to interact with other chains, thus increasing its use and value. Bittensor and TaoPad positively address the questions of integrating AI and Blockchain, providing an excellent example of how blockchain can provide a structure for AI development and, at the same time, AI can generate value through the blockchain. They also offer a great incentive for users with different interests to participate in projects involving similar integrations, allowing them to contribute to the evolution of this technological symbiosis.
WRITTEN BY: Elena Temperini




评论 (0)